To comply with environmental regulations, computers are equipped with power-saving mechanisms. These mechanisms turn off different hardware parts (CPU, HDD), which may cause performance problems during long-lasting tasks.
For such tasks, the following power-saving options should be adjusted:
BIOS power options
MS Windows Power Options
CPU power modes (C States or C Modes) which can be turned off either in BIOS or Windows REGISTRY
Depending on the manufacturer, adjusting the BIOS settings may change the corresponding settings in Windows and vice versa. However, we recommend to make sure the settings are correctly set in all the places.
Caution
Some IT departments override the Windows Power Options settings when a domain-included computer starts, so you may want to verify that the settings persist after your PC reboots, or when you login under a different user account.
BIOS version: 1.65
Enter BIOS by pressing F10 and set the following settings.
Go to the Advanced tab and click Power Options.
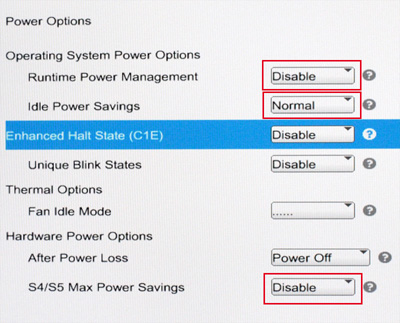
Set the Power Options as displayed in the following image.
Runtime Power Options: Disable
Idle Power Settings: Normal
S4/S5 Max Power Savings: Disable
Return to the Main tab and save the changes:
BIOS version: 1.65
Note
This procedure was tested on a dual-processor machine. A single-processor Z840 setup may differ.
Enter BIOS by pressing F10 and set the following settings:
Go to the Advanced tab and click Power Options.
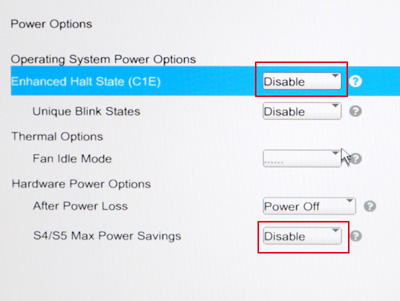
Set the Power Options as displayed in the following image:
Enhanced Halt State (C1E): Disable
S4/S5 Max Power Savings: Disable
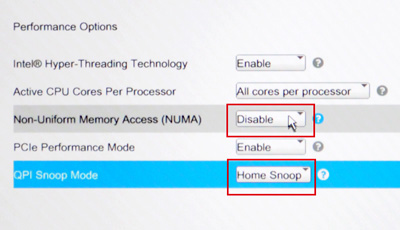
Go back to the Advanced tab and set the Performance Options as displayed:
Non-Uniform Memory Access (NUMA): Disable
QPI Snoop Mode: Home Snoop
Return to the Main tab and save the changes:
BIOS of other PC models / manufacturers will likely differ from the ones described. Here are some general rules which can help you:
Enter BIOS during startup of MS Windows. Please, consult the PC/motherboard manual or the "boot screen" on how to enter BIOS. It can be e.g. by pressing the F10 key.
Disable or toggle all power-management settings related to CPU Speed, USB and PCI/PCI-Express bus.
Example of setting names:
SpeedStep
Throttling
Dynamic performance
C-States Control
Idle Power Savings (change this to "Normal")
Disable unused onboard devices. Computer motherboards can contain many built-in devices which usually use resources even if they are not in operation. If you do not use them regularly, turn OFF all such devices:
FireWire controllers
WiFi controllers
BlueTooth controllers
Click the Start menu. Type “Control Panel” in the search bar and select it.
In the Control Panel window, make sure the View by > Small Icons option is selected. Click Power Options.
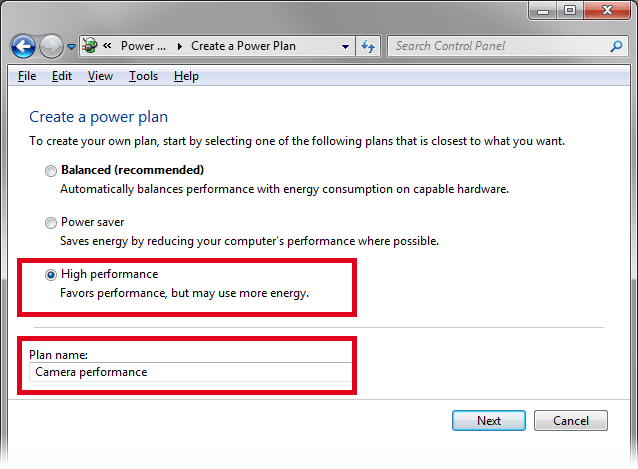
To create your own power plan, click Create a power plan.
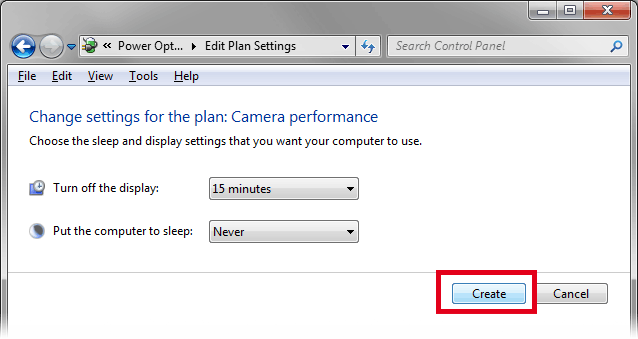
A window appears, select High performance. Your power plan will be based on it. Name your power plan. Click .
Click .
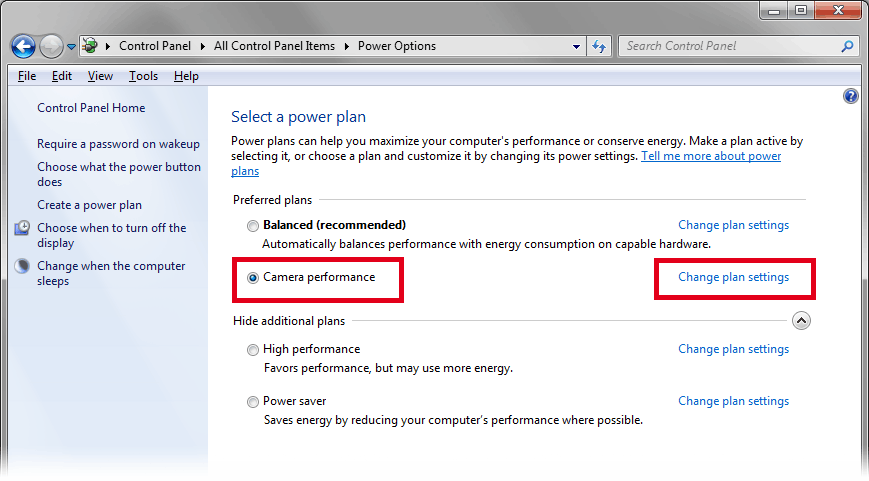
Your power plan appears in the list. Select it and click Change plan settings.
In the next window, click Change advanced power settings.
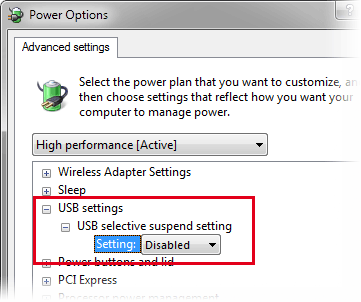
Set USB settings > USB selective suspend setting to “Disabled”.
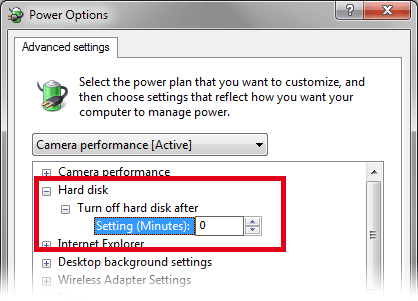
Set Hard disk > Turn off hard disk after to 0.
0 stands for “never”.
Save and close all windows by the buttons.
The above procedure will work if the High performance power plan is in its factory setting. If you want to be sure, check whether all the following settings are set correctly:
Table 6.
| Setting | Value |
|---|---|
| Hard Disks > Turn off hard disk after | 0 (Never) |
| Sleep > Sleep after | 0 (Never) |
| USB Settings > USB selective suspend setting | Disabled |
| PCI Express > Link State Power Management | Off |
| Processor power management > Minimum processor state | 100% |
Log into Windows with an administrator account.
Navigate to your CState folder where NIS-Elements is installed. Typically:
C:\Program Files\NIS-Elements\Drivers\CStateRun
disableCstates.bat.Restart your computer.