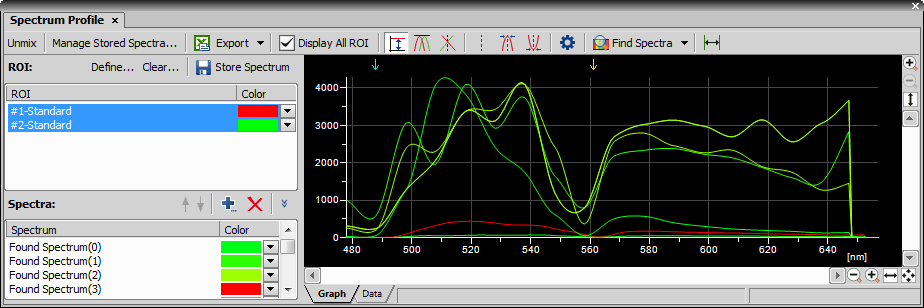
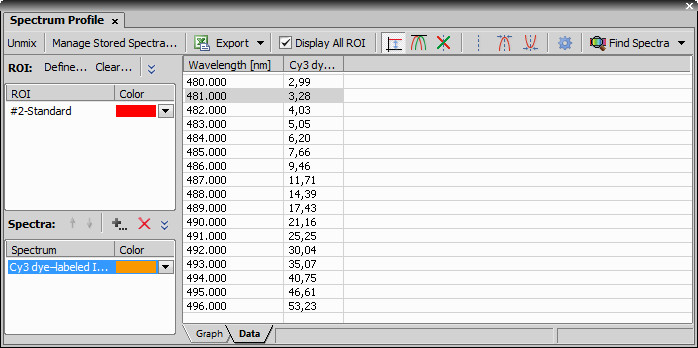
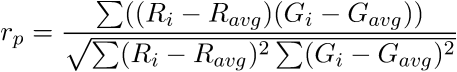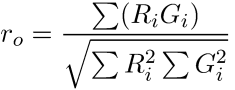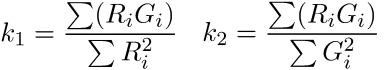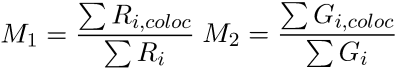Selecting commands from the command history.
Removing redundant commands - decide whether to remove doubled commands or not.
Adding, removing, or editing chosen commands.
Finishing the Paste History wizard.
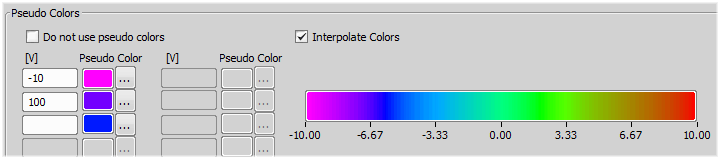
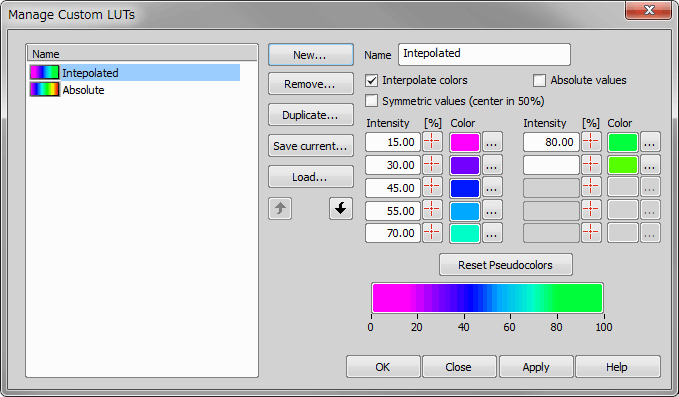
Deselect the Do not use pseudo colors check-box.
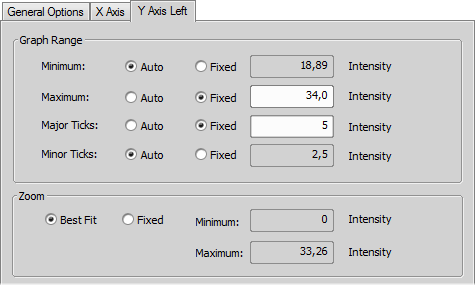
Insert values out of the calibration units range to the left column and select a color for each of the value.
An automatic algorithm will create a spectrum-based color scale between the defined values.
Note
The system reads the voltage range available to the device and extrapolates the color scale to this range. In other words, the minimum and the maximum of the color scale corresponds to the min/max voltage of the device according to the defined calibration.
Click on the Configure / calibrate
 button to open the configuration dialog and click on the button.
button to open the configuration dialog and click on the button.Select the type of calibration slide you will use:
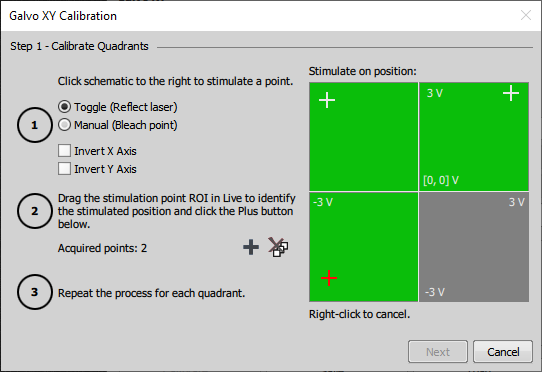
Toggle (Reflect laser)When you click in a quadrant, laser will be turned on until a right-click.
Manual (Bleach point)Click a point and hold the mouse. When released the laser turns off.
Add at least one calibration point in every quadrant, preferably in the outer corners. After adding a calibration point, move the point ROI in the live image to the laser spot and press the
 button to store the calibration.
button to store the calibration.Caution
If the FOV of your camera is smaller than the galvo XY range, the stimulation may not be visible in the live image. In such case, try placing the stimulation point closer to the center.
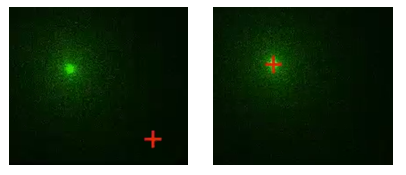
Click . Another dialog appears. Here you can use the button to test the calibration. Move the red cross around the live image and and activate the stimulation by this button. Click to finish the calibration.
Consider saving the current calibration to a XML file by the button.
Click either the Coarse or Fine button which you want to define the step of.
Fill the desired value to the edit box in the middle. The value is set and remembered.
Fill the coordinates of the new position in the edit box(es).
Press the Move button.
Move Z to requested position.
Change exposure of a camera and click the
 button.
button.This position is added as a new record to the list of positions for Z corrections.
Repeat to define another Z position. You have to define only few reference Z points which are interpolated in the result.
 Insert Text
Insert Text Insert Arrow
Insert Arrow Insert Labeled Arrow
Insert Labeled Arrow Insert Line
Insert Line Insert Rectangle
Insert Rectangle Insert Ellipse
Insert Ellipse Insert Polyline
Insert Polyline Insert Polygon
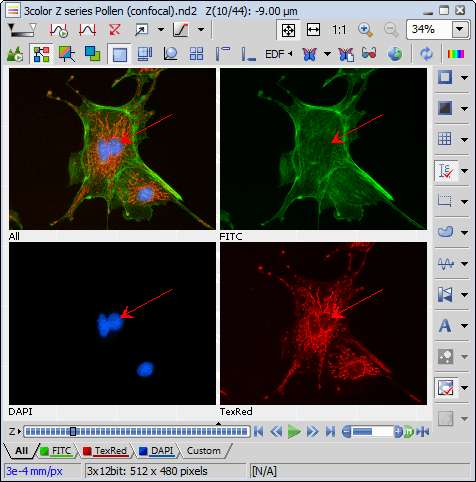
Insert PolygonSelect the channels to be included in the calculation from the pull-down menus.
Scattergram is displayed inside the control window.
Colocalization coefficients are displayed at the bottom.
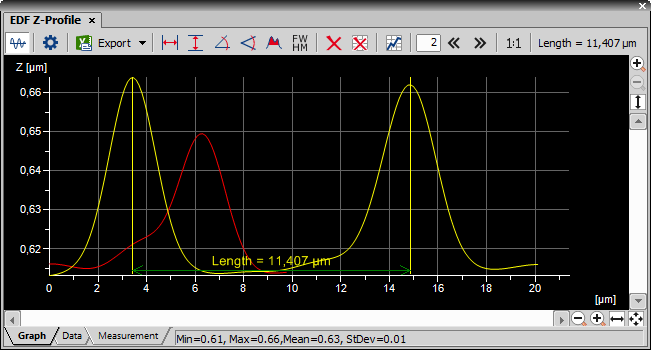
Click the View > Analysis Controls > EDF Z-Profile
 command to display the control window
command to display the control windowOpen an ND2 file containing the Z dimension.
Use the Applications > EDF > Create Focused Image
 command.
command.The graph appears in the control window automatically.
To add more profile lines to the image, use the context menu over a profile line and select Add Z-Profile Line.
To remove an existing line, use the context menu over a profile line and select Remove Z-Profile Line.
To change the appearance of a profile line, use the context menu over the line and select Line Properties....
Intensity
Channels
Hue, Saturation, Intensity
Ratio
In the View > Analysis Controls > Automated Measurement
 panel, click the Update Measurement
panel, click the Update Measurement  button to measure the current image. For a multi-dimensional image, use the Keep Updating Measurement
button to measure the current image. For a multi-dimensional image, use the Keep Updating Measurement  button to make sure that data of the current frame are always displayed.
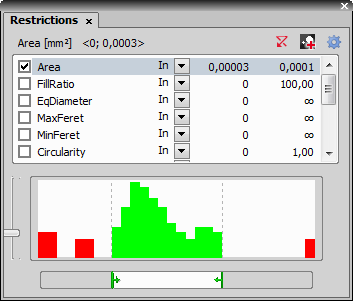
button to make sure that data of the current frame are always displayed.Right click to the restrictions field to select one or more of the measurement features.
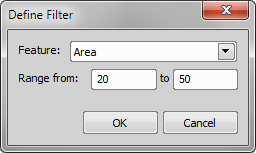
Select the restriction feature you would like to define. Name of the selected feature appears above the table. The current interval of possible values is indicated next to the feature name.
The limit values are indicated next to the feature name in the table, and can be modified directly by double clicking the indicated value. The infinitude can be defined by entering “oo” or “inf”.
Use the histogram and its controls in the bottom part of the control window to directly change the restrictive values. The slider on the side changes proportional height of the histogram. The two independent sliders below the histogram set the lower and upper limit value of the selected measurement feature. The accepted values are marked green. The restricted values are red.
Decide whether the defined interval will be excluded or included from/in results. This is done by setting the Inside/Outside value next to the feature name.
The nearby check box indicates whether the restriction is applied or not. If applied, the histogram below is color, otherwise it is gray.
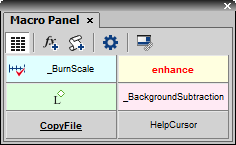
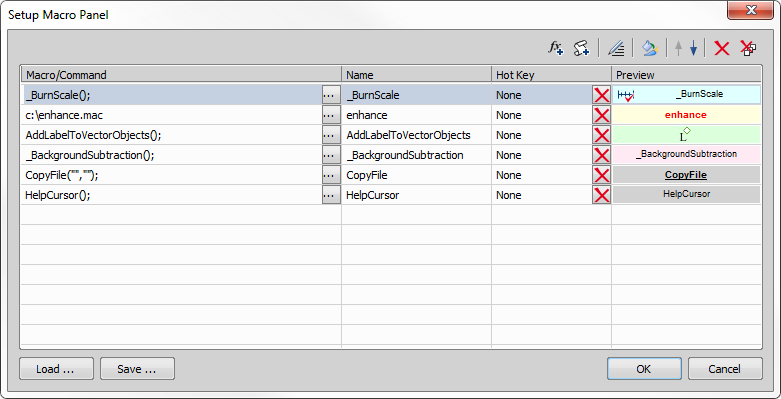
Press the
 button.
button.Select a command from the Paste Command window. And press OK.
Selected command is inserted in the Macro Panel window.
Right-click the command and select the Properties command from the context menu. Change appearance properties (used bitmap, font properties, etc.) of the command's button and confirm.
Press the
 button.
button.The Add Macro window appears.
Select a macro. The Predefined, Shared and Recently used macros are listed in separate sections. When you need to import a macro from file, press the
 button and choose proper file. To select multiple macros, use the
button and choose proper file. To select multiple macros, use the  button to select them all within a section, or check their individual check-boxes.
button to select them all within a section, or check their individual check-boxes.When necessary, use the
 command to edit the selected macro in the Macro Editor.
command to edit the selected macro in the Macro Editor.Confirm by pressing the OK button.
Selected macros are inserted in the Macro Panel window.
Right-click the command and select the Properties command from the context menu. Change appearance properties (used bitmap, font properties, etc.) of the command's button and confirm.
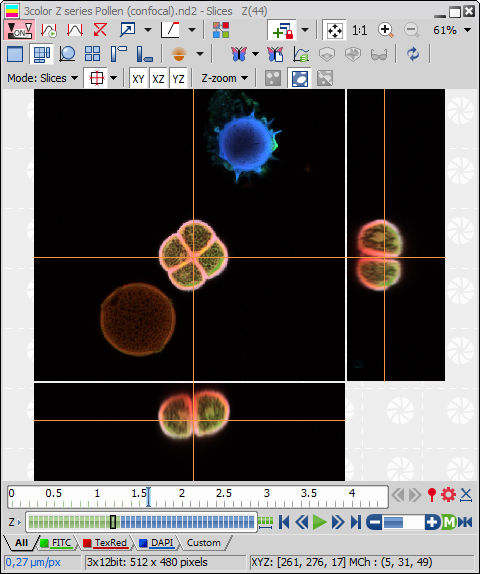
Display the cross by the Show Cross button. You can select to display a small or large cross. If the
 Add View to Synchronizer function is turned on in multiple slices views, the cross position is automatically synchronized among them.
Add View to Synchronizer function is turned on in multiple slices views, the cross position is automatically synchronized among them.Place the section lines anywhere in the image.
Choose different display mode from the menu which appears when you press the Mode button. Slices, maximum and minimum intensity projection view are available.
The YZ and XZ views are available on sides of the common XY view. Any of the view can be hidden/displayed. Deselect the proper button (XY, XZ, YZ) to hide the view.
The XZ/YZ views can be enlarged/reduced by selecting Z-zoom.
A new image can be created from either the YZ or XZ view. Right-click the view and select Create New Image From This View from the context menu.
Binary, color, overlay layers and ROIs can be displayed using corresponding buttons.
A color scale can be displayed in channel, Ratio, FRET, or Calcium views by a command from the context menu. You can change color of the scale or convert it to a gradient (available for FRET and Ratio views). If 3D binary objects are defined, it is possible to colorize them on the context menu (Colorize Binary by 3D Objects).
Time is rescaled if there are 2 Time phases with different Time Intervals and Time Durations.
EDF Z-profile showing the Z profile line of the current slice can be shown/hidden using a context menu function (Show/Hide EDF Z-Profile).
Manual length measurement in 3D inside the slices view can be performed using
 Length 3D from the menu View > Analysis Controls > Annotations and Measurements
Length 3D from the menu View > Analysis Controls > Annotations and Measurements  . See also 3D describing details about the 3D length measurement.
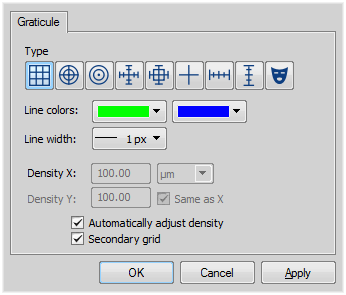
. See also 3D describing details about the 3D length measurement.  Rectangular Grid
Rectangular Grid Circle
Circle Simple Circle
Simple Circle Cross
Cross Industrial Cross
Industrial Cross Simple Cross
Simple Cross Vertical Ruler
Vertical Ruler Horizontal Ruler
Horizontal Ruler Graticule Mask
Graticule MaskFont type
Size
Alignment
Vertical Alignment
Style (Bold, Italic, Underlined)
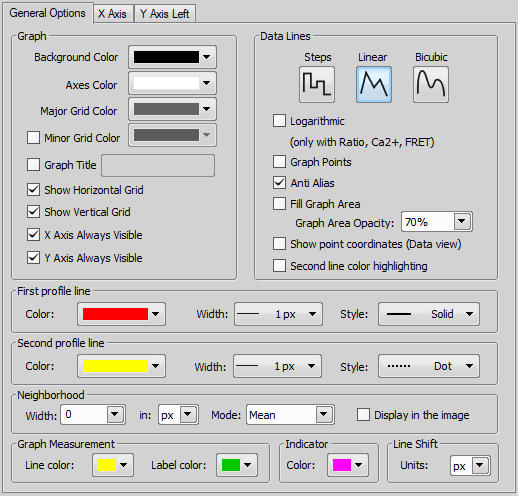
Mean - mean intensity of the stripe width is displayed in the graph
Max - maximum intensity of the stripe width is displayed in the graph

This command switches NIS-Elements application to Organizer Layout (See Organizer).
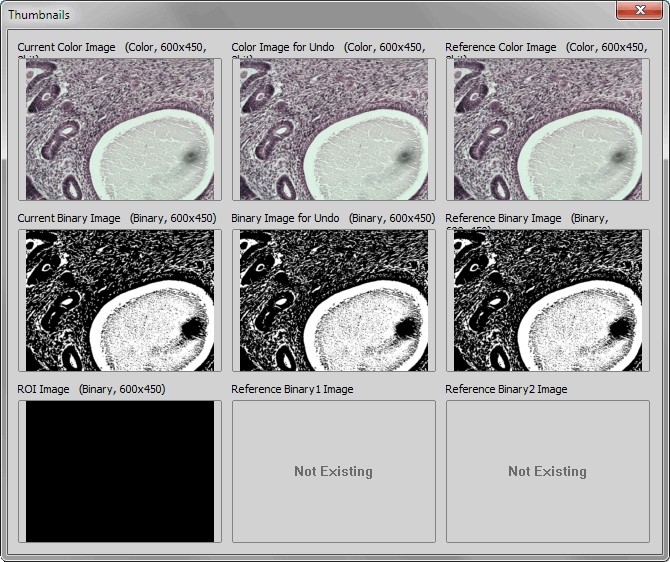
The Thumbnails command displays all working images (reference, current, images for undo...) at reduced size.
NIS-Elements can store temporarily a number of reference images to memory. They can be recalled later, or image arithmetic operations can be performed combining the current and the reference images. All the related commands can be found within the Reference menu.
Displayed Thumbnails
The currently active image.
The last image saved automatically to the Undo History.
The reference image added by user via the the Reference menu. See Reference > Current Image -> Reference.
The currently active binary image.
The last binary image saved automatically to the Undo History.
Commands from within the Reference menu were used to copy binary images to these positions. However, this functionality has been replaced by advanced commands which work with multiple binary layers. See Binary > Binary Operations, View > Analysis Controls > Binary Layers  .
.
The current color and binary image can be copied into the Reference and Measurement ROI positions using the commands from the Reference menu. The Current and for Undo images are obtained automatically.
This command saves changes of the current layout.
See Also
Arranging User Interface
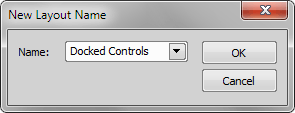
This command saves the current NIS-Elements layout under a different name. The following dialog box appears:
Type the new name in or select one that is already in use and confirm it by .
See Also
Arranging User Interface
This command saves current layout and sets it as default.
This command reloads the current layout settings. It discards changes made from the time it was last saved.
See Also
Arranging User Interface
This command opens the Layout Manager - a NIS-Elements layout administration tool. Please see the User Interface chapter for more details.
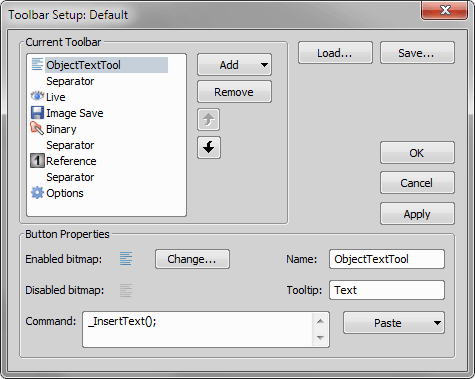
Configures a toolbar.
Displays list of icons (command) in current toolbar.
Adds a new toolbar command or a separator.
Removes currently selected command.
Changes the order of icons on the toolbar.
Displays icons in enabled and disabled state together with associated command.
Press this button to change the image associated to command.
Write command name (or name of more command), that should be associated to current toolbar button.
This submenu helps to insert commands into the command edit box. Choose whether to:
Opens the list of all available commands. Choose the one you would like to insert.
Opens the Macro - Open dialog box in order to define a macro to be executed.
Pastes the sequence of recently used commands in four steps:
Displays name of current toolbar entry.
Displays tooltip, that will be displayed when you move over the toolbar button by mouse.
See Also
View > Customize Toolbar > Next, View > Customize Toolbar > Previous
 , Right
, Right  , Bottom
, Bottom 
These commands display/hide the selected docking pane. A docking pane enables you to group control panels (e.g. Histogram, LUTs, Camera Settings, etc.) to one side of the screen.
See also Docking Panes.

This panel is described as a part of the Compact Layout (Compact Layout).

(requires: Local Option)
Opens the Alveole Primo dialog window.
Opens the AOTF Pad. Please see AOTF via NIDAQ - Illumination Device.

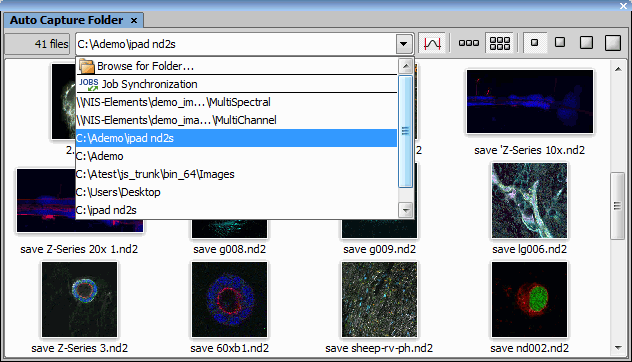
This control window displays the content of the Auto Capture Folder. This folder is used by the File > Open/Save Next > Save Next  and Acquire > Auto Capture
and Acquire > Auto Capture  commands to store images.
commands to store images.
 Browse for Folder...
Browse for Folder... The destination directory can be changed by clicking the Select Directory button in the combo box and search for a new folder. The setting is global for the File > Open/Save Next > Save Next  and the Acquire > Auto Capture
and the Acquire > Auto Capture  commands. List of recently used folders is displayed below the
commands. List of recently used folders is displayed below the  Browse for Folder... and
Browse for Folder... and  Job Synchronization items.
Job Synchronization items.
 Job Synchronization
Job Synchronization This virtual folder automatically shows the images acquired by the last launched job.
Number of images in the folder is indicated in the top left corner of the control window.

 wrapping,
wrapping, 


 thumbnail size
thumbnail size Image thumbnails can be lined up in a single row or in multiple rows using the wrapping buttons. Number of rows depends on the selected thumbnail size and on the size of the control window. Size of image thumbnails can be easily changed using the thumbnail size buttons.
 Apply autocontrast to thumbnails
Apply autocontrast to thumbnails Press this button to apply LUTs autocontrast function to the displayed thumbnails.
Caution
Using this function, two almost-identical images may look different (brightness-wise). For example if the same scene is captured with and without a scale, the scale may cause the thumbnails to look differently.

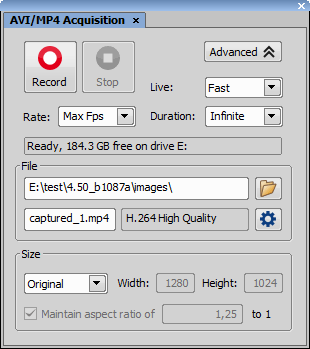
This control window contains tools used for creating an AVI movie. Creating movies is an efficient way how to present your image data outside the NIS-Elements application.
See Capturing AVI Movie for more information.

This commands adjusts parameters of the currently used camera. The Camera Settings control window appears.

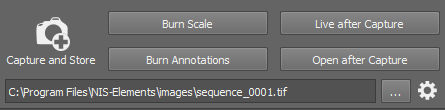
This control panel contains a single button which captures an image and saves it to a folder according to the settings:
Press the ... button and select the folder where images captured by the  Capture and Store button will be saved. The path and file name of the next image to be saved is displayed on the left.
Capture and Store button will be saved. The path and file name of the next image to be saved is displayed on the left.
Select which vector layers will be burned into the saved images. We recommend to use these options only if saving the captured images to a file format which is not capable of saving vector layers (bmp, png, ...). See also Supported File Formats. Note that mono images are automatically converted to RGB images after the scale/annotation is burned. Image data and quantitative information can be lost.
Displays live image after the  Capture and Store button is clicked.
Capture and Store button is clicked.
Select this option to open each captured image in NIS-Elements.
 Capture and Store
Capture and Store Click this option and a new image will be captured and saved to the directory specified above.
 Settings
Settings Type the prefix and numbering style intended for the files being saved automatically. The Next File field informs you and enables you to change the number which will be used for the next image saved automatically.
Select the file format to save the images in. Some formats enable you to set the Compression parameter. It is recommended to use either “none” or “lossless” in order to preserve good image quality.
The images can be sorted to subdirectories automatically based on the time of acquisition. Select this option and use place-holders to specify format of the folder names (click  to display a list of available place-holders). E.g.: “$YYYY$MM$DD” would create a new subdirectory for each day named like this: “20170103”.
to display a list of available place-holders). E.g.: “$YYYY$MM$DD” would create a new subdirectory for each day named like this: “20170103”.

(requires: CA FRET)
Display and use this control window to capture a FRET image. You get an easy access to all settings and tools via this control window.
See FRET for further explanation of all controls.

(requires: 6D)
The ND acquisition window enables you to set-up and run a multi-dimensional experiment. Please see Combined ND Acquisition.

(requires: 6D)
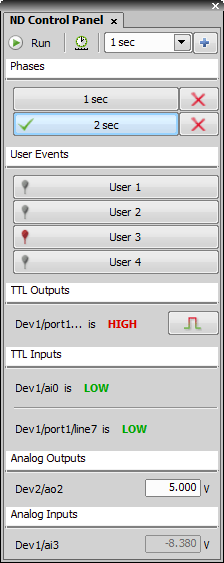
This window enables you to control the current ND experiment and visualize and control analog/digital input and output signals. The NIDAQ controller set is required to be able to perform the inputs/outputs functionality. The window displays only lines installed (added) within the NIDAQ physical device configuration. See Devices > Device Manager  .
.
Control Window Options
This button runs the current ND experiment and then turns into the Finish button which breaks the acquisition progress and saves the data set acquired so far.
 Perform Time Measurement
Perform Time Measurement This button corresponds to the Perform Time Measurement option within the ND Acquisition window.
 Add New Phase
Add New Phase This button enables you to quickly add a new time phase to the experiment. Select the acquisition interval from the pull-down menu and click the button. A new phase will be appended to the list of phases. Duration of phases added by this button are set to Continuous by default so the acquisition is expected to be controlled via ND control panel.
This section displays two buttons for each time-phase defined in the ND experiment. The first button selects the clicked time-phase which means that the phase will be the starting phase when the acquisition is started or, in case the acquisition is already running, the preceding time-phases will be skipped and the acquisition will continue with this phase.
The second button  deletes the phase from the list. This operation can not be undone.
deletes the phase from the list. This operation can not be undone.
Each button in this section represents one user event. Every time it is pressed during ND acquisition, a notification is inserted to the ND2 file meta-data. Moreover, a macro command can be run at the same time. Right-click one of the buttons and select Edit Events from the context menu. A window appears where you can specify events properties. See also Special Options.
Note
This section appears only if at least one user event is defined and the Show on Toolbar box is selected.
Names and current signal state (LOW or HIGH) of all active input/output lines are displayed in this window. You can send output signals by the buttons on the right. The action which will be performed depends on the actual settings of the output line (within the device manager).
Names and signal values of all active input/output lines are displayed. You can adjust output signals by inserting a voltage value into the edit box on the right. The new voltage will be established upon pressing Enter.
Functionality of calibrated inputs/outputs corresponds to the non-calibrated lines except that instead of voltage [V], they can display or accept any units. This of course depends on the calibration. To calibrate a line, right-click its name and select Calibrate Analog ... command from the context menu.
Note
There are three ways to visualize the line state. Right-click the line name and select one of the ways - Value Only, Slider and Value, Color Box and Value.
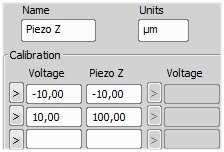
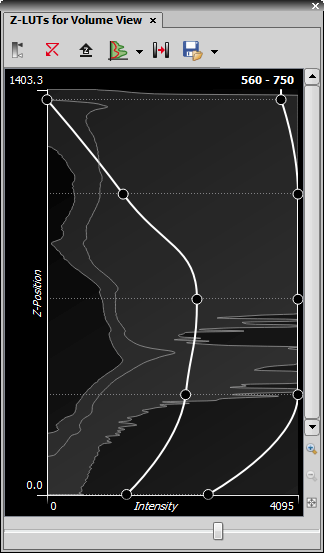
Analog Input/Output Calibration
After you select the Calibrate Analog ... command from the context menu, a two-section window appears. The top section enables you to define the calibration - in other words to map voltage values of the device to values used within the software. First of all specify the calibration name and units. Afterwards, enter as many voltage-yourUnits pairs as needed to the edit boxes. If the connected device behavior is linear, two pairs are enough. You can also insert the current voltage value by clicking the button.
The calibration curve is displayed on the right side as you type the values in. Different interpolation methods can be selected from the pull-down menu.
Color indication of the current input/output value may be also defined. Either the value range is indicated by a gray-scale, or custom pseudo colors may be defined:

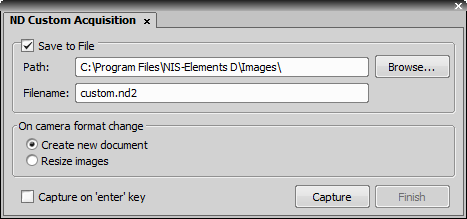
Performs manual user acquisition based on single captured images of an experiment. Press the Capture button to capture each frame. An ND2 file is created from the sequence of captured images after you press the Finish button.
Check this item to save the image in a file. Specify the destination folder and name the file.
This option defines an action which should be done when camera format (resolution) has changed during the experiment. There are two possibilities: either a new image is created or the image is resized.
Check this option to assign the Enter key to the Capture action.

(requires: 6D)
This control window defines the multipoint acquisition via setting an ND experiment.
See Multi-point Acquisition for detailed information.

Use this control window to define ND stimulation experiment. For more information see Applications > 6D > Define/Run Simultaneous Stimulation.

Opens the Nosepiece pad of the manual microscope (see Nikon MM 400/800 Microscopes).

(requires: Local Option)
This pad controls the assistance observation camera, which can be operated even if two cameras are already connected to NIS-Elements. This pad is primarily used in the TIRF configuration for observing the “Back Aperture Plane” through the camera. The list of supported cameras is next to the button. Currently supported cameras are Basler and Imaging Source.
Select the camera and click to connect it. In the right drop-down menu choose whether to display the normal camera image, its inverse Fourier transform, or both. Below select the zoom to center magnification (1x - 6x).
 Live runs the live image whereas
Live runs the live image whereas  Capture captures the current image. The last image taken is being exported to the document. Gain and LUTs (LUTs - Non-destructive Image Enhancement) can be adjusted below.
Capture captures the current image. The last image taken is being exported to the document. Gain and LUTs (LUTs - Non-destructive Image Enhancement) can be adjusted below.
Note
Observation camera plugin (requires: Local Option) has to be installed in order to use this pad.

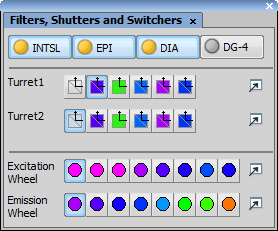
This control window provides an overview of filters, shutters, and laser switchers within the system. The devices can be operated from this window.
Shutters
All available shutters are listed on the device toolbar (part of the top application toolbar).
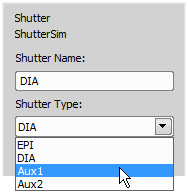
You can open / close an operating shutter by clicking on its icon. When you right click the shutter button, a contextual menu containing the Shutter Parameters command appears. Click the command to display the following window:
Define a new name for the shutter and select the proper type of the shutter (EPI, DIA, Aux1, Aux2). You can display this window also from the Device Manager or Microscope Pad.
Filters
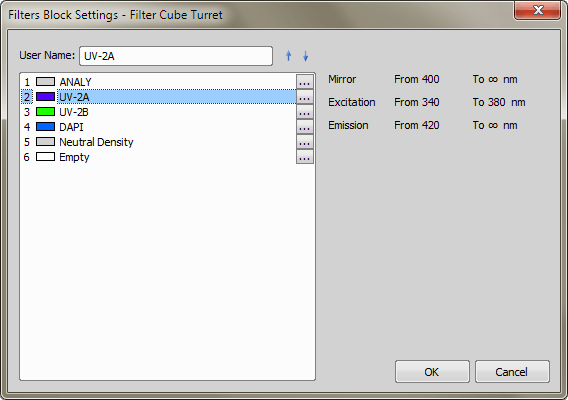
Press the button which corresponds to the filter you want to use. A filter settings can be changed after you press the  button in a Filters Block Settings window:
button in a Filters Block Settings window:
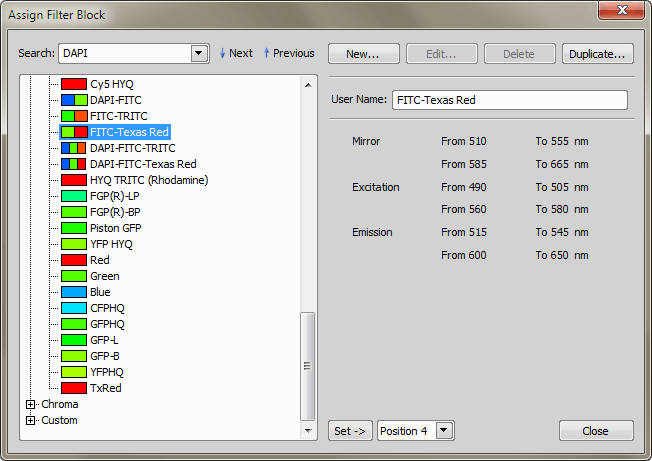
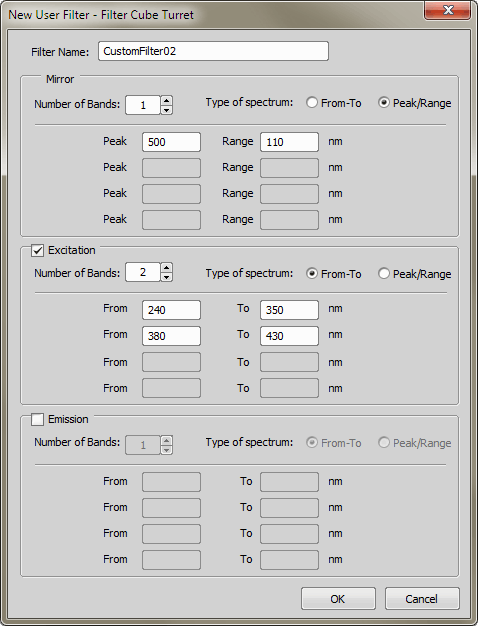
All filters present in selected filter turret are listed in this window. Available filter information as Excitation, Mirror and Emission wavelengths are displayed in the right part of the window. You can select a different filter from a Filter Blocks Database which appears when you press the ... button in the Filters Block Setting dialog window:
Use commands in this window to manage filters. Filters in the Nikon and Chroma thread are predefined filters and can not be edited. Custom filters are defined by the user and are editable. Select a filter from the database. Enter the name to the Search box and press the  Next or
Next or  Previous button. Information about currently selected filter are displayed on the right side of the window. You can also add a New custom filter, Edit existing custom filter, Delete it or Duplicate it. Press the Set button to assign selected filter to the selected turret position.
Previous button. Information about currently selected filter are displayed on the right side of the window. You can also add a New custom filter, Edit existing custom filter, Delete it or Duplicate it. Press the Set button to assign selected filter to the selected turret position.
Displays editable filter name.
Check which settings is used for defined filter.
Specify number of used bands.
The spectrum can be defined by setting the from-to wavelength values, or by setting the peak value and the range of wavelengths. The number of text boxes depends on number of bands used.

(requires: Illumination Sequence)
This window displays the Illumination sequence dialog window. For more information, please see: Illumination Sequence.
(requires: XY Galvo device)
If you have the XY Galvo device module enabled, several galvo-mirror-based stimulation devices become supported. Devices of several manufacturers are supported.
See also Cameras & Devices.

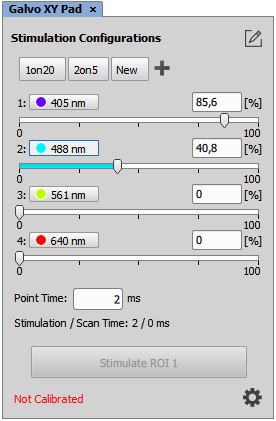
Click this button to display selection boxes in front of the laser lines. De-select lines to be hidden on the pad. Click the button again to exit the edit mode.

Saves settings of the pad to a preset. Enter its name and click . A button with this name will be created, click it to load the settings.
The time that every pixel in the stimulation ROI is illuminated.
This performs the stimulation on all ROIs associated with the current stimulation configuration. To activate one ROI only, click on the Stimulate button next to the ROI within the image.

Opens a configuration dialog window.
If you have one of the listed products, select it. The Volts low and Volts high values will be filled automatically.
Select your NIDAQ board model used to control galvo xy. Available ports will be ch
Available connector blocks for the selected NIDAQ board can be listed. If you select it, port names in the other pull-down menus will be renamed accordingly.
Select NIDAQ ports which control the mirrors.
Maximum and minimum values which can be set to the device.

Sets mirrors to position 0, 0 V.
You can enter arbitrary voltage to the edit boxes. This button sets the voltage to the device.
Select the port which sends the TTL High signal whenever the stimulation is active.
Select the port for external triggering of stimulation.
If the device is equipped with a pulse laser, select the line which controls it. A new slider called Ablation Frequency will appear in the pad.
Opens the calibration window. See Galvo XY Calibration.
Saves the current calibration to an XML file.
Loads the calibration from an XML file saved on a hard drive.
Galvo XY Calibration
(requires: XY Galvo device)
The device must be calibrated manually so that the mirrors are aimed at correct XY coordinates in the image.
Note
If the user changes some system settings (e.g. selects a different objective, zoom or confocal scanning mode), the current calibration may become inaccurate and the stimulation area may shift. In such case, a new calibration should be performed.

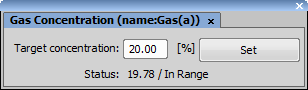
(requires: Stage Incubator)
This command displays a control pad of the connected incubator. Depending on the particular model/manufacturer, the pad can be used to set target values (heat/gas concentration/humidity) and to view the current values.

(requires: Well Plate Loader)
Opens the Well Plate loader control window.

(requires: N-STORM Analysis)
Opens the N-STORM dialog window for acquisition of STORM images. For more information please see N-STORM Acquisition and Analysis.

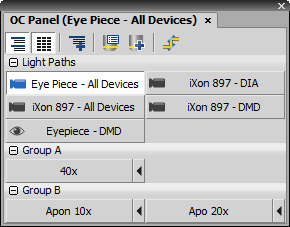
This control window manages and overviews optical configurations defined and used by the application.
Control Window Options
 Show Groups
Show Groups Press this button to sort the optical configurations displayed in the control window to groups. These groups can be expanded or collapsed by the +/- buttons next to the group name.
 Regular buttons
Regular buttons After you press this button, all optical configurations button stretch to the same size.
 New Group
New Group Press this button to create a new group of optical configurations.
 Explore Optical Configurations
Explore Optical Configurations Opens the Optical Configurations window. See Calibration > Optical Configurations  for further description.
for further description.
 New Optical Configuration
New Optical Configuration Opens the New Optical Configuration window. See Calibration > New Optical Configuration  for further description.
for further description.
 Lightpath Scheme
Lightpath Scheme Opens the Lightpath Scheme pad showing the current microscope configuration with visible light paths.
These buttons represent available optical configurations which are placed on the Optical Configuration toolbar. Press the corresponding button to select/unselect an optical configuration. Channel color for optical configuration is displayed next to each of the buttons. If you press the black arrow button, current camera and device settings will be assigned to the selected optical configuration.
Context Menu over Toolbar and Groups
Creates a new OC group with a given name.
Renames the group over which the user is inducing the menu.
Regular buttons can be turned on/off using this command.
Groups can be shown/hidden using this command.
Color next to each channel can be shown/hidden using this command.
Displays/hides the black arrow next to each OC button, used for assigning the current settings.
This command shows/hides the main toolbar containing control buttons.
This command can be used to lock the current size of the window. The window cannot be resized until the geometry is unlocked again.
All OC buttons can be shown in the main toolbar using this command.
Opens the Properties dialog where the font type, font size, font style, and text and background colors of the OC buttons can be changed for the current group.
Context Menu over OC buttons
Assigns the current objective to the selected OC.
Assigns the current camera setting to the selected OC.
Assigns the current microscope setting to the selected OC.
Opens the Properties dialog window enabling to adjust the type, size, style and color of the font including the background color of the selected OC button.
Reveals a context menu described above.
Calibrates the selected OC using the current objective.
Selects/deselects the OC button.
Copies the settings of the current OC to the OC chosen from the context menu.
Copies the selected OC into a new OC with a given name.
Opens the New Optical Configuration dialog window enabling to define a new OC which is then added to the OC Panel.
Removes the selected OC from the OC Panel.
Renames the selected OC.
Opens the Optical Configurations dialog window enabling to edit the selected OC.

Opens the Piezo XY Pad used for controlling the piezo XY stage. Adjust the X/Y sliders to move the stage in the particular axis direction or set the value in the edit box and click . The  button returns the stage to its home position.
button returns the stage to its home position.

Displays the Real Time EDF control panel. See Real Time EDF.

This panel displays overview of the current sample and makes the navigation on it easier. Please see Sample navigation .

Please see Shading Correction.

Opens the Ti2 LAPP Pad. For more information please see View > Acquisition Controls > LAPP Pad.
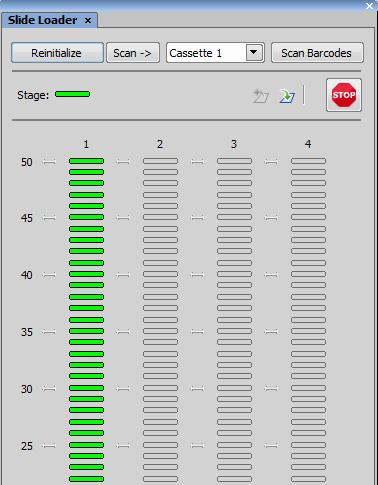
(requires: Slide Loader)
This command opens the Slide Loader control window.
This button initializes the slide loader and retrieves information about slides and cassettes present in the device.
Starts scanning of slides of all cassettes present in the loader.
Scans bar codes of all slides.
Indicates the current stage state (empty or loaded).
Removes the slide currently loaded on the microscope stage and returns it to its original position.
If some unexpected event occurs or a crash is at hand, press this button to stop the slide loader immediately.

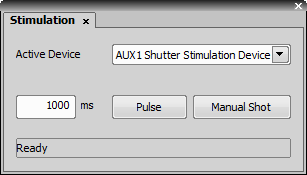
This window controls the stimulation devices. Select the active device from the pull down menu. Set the duration of the stimulation phase in the editable field and use the Pulse or Manual Shot buttons to start the stimulation.

Displays the control pad or the control full pad of the connected microscope.

(requires: RT Acquisition)
Triggered Acquisition control window sets the fast camera-triggered experiments. Please see Acquisition Settings

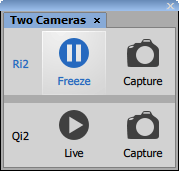
Opens the Two Cameras panel which can run the live signal and capture images on two cameras connected to a single port through a Dual Camera splitter. The highlighted camera name indicates the active camera which can be controlled in the NIS-Elements top toolbar. Active camera can be changed by clicking on its name.

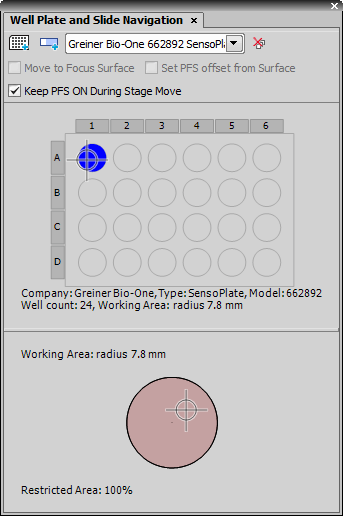
 Add Well Plate...
Add Well Plate... Opens the Select Wellplate window, where you can select a well plate from the list.
 Add Slide...
Add Slide... Opens the Select Slide window, where you can select a slide from the list and define its orientation on the stage.
 Remove All
Remove All Can be used to remove well plates/slides from the list.
If moving to a well/slide position, the Z drive moves not only to the XY position but also to the Z focus surface position defined by the Focus Surface (see: View > Acquisition Controls > XYZ Overview  ).
).
If checked, this function uses a PFS Offset value for the current well/slide position based on the active PFS surface (see: View > Acquisition Controls > XYZ Overview  ).
).
Check this item to keep PFS on during stage movement.

(requires: Stage)
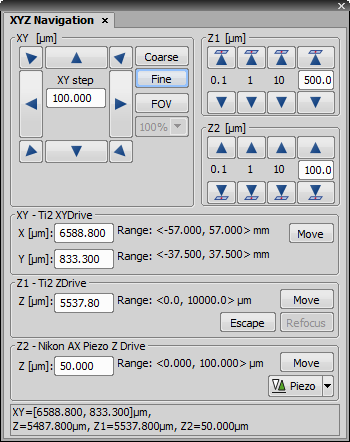
If a motorized stage and / or a Z drive is present in the system, their positioning can be controlled using this panel.
Relative Movements
Two accuracy settings of movement can be set to Coarse or Fine. Whenever an arrow button is clicked, the stage moves by one step in the selected direction. Moving the stage in a diagonal direction, e.g. top-right direction, behaves like if the top and right moves are performed together. The current step size is displayed between the arrow buttons.
Note
Each physical device has its minimum step size. If the step value set in the edit box is smaller than this minimum, the device will move by the minimum achievable step without warning.
If you pressed the FOV button, the step size is calculated automatically in order to match the current camera field of view. The below pull-down menu reduces the calculated step size by the given percentage.
Click the arrow to move the Z drive in the indicated direction with the predefined or custom step size. The arrow button with a sample ( ) indicates the Z drive direction moving towards the sample.
) indicates the Z drive direction moving towards the sample.
Note
Some stages require Z calibration before Z navigation can be used. If your Z control is disabled (N/A), calibrate the stage using Devices > Calibrate Z.
Absolute Movements
You can move the stage(s) to any position by giving the system its absolute coordinates.
Moves Z drive to its escape position.
Moves Z drive to the previously set refocused position.
Available only when Piezo Z drive device is connected. Press the arrow button to open a submenu and select an action. This action is performed when you press the Piezo button. The Keeps Z position and centers Piezo Z option moves Piezo Z drive to the home position, but keeps the original position of absolute Z (sum of Z1 and Z2). The Move Piezo Z to Home position moves Piezo Z drive to the home position, regardless of Z drive position.

(requires: Stage)
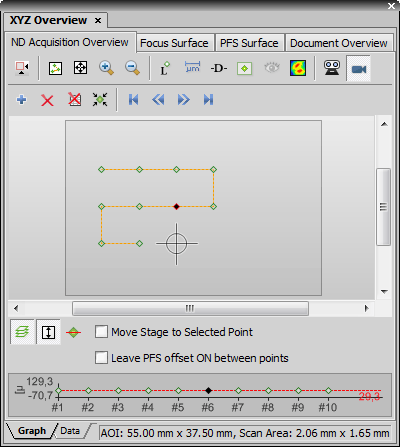
Displays the the  XYZ Overview panel:
XYZ Overview panel:
The window consists of the tabs, each one designed for a different use:
Provides overview of the whole stage with the defined experimental points. It enables the user to modify, add and remove points, which are to be captured during the experiment.
Overview Elements
Selected point is black. All other unselected points are green.
A line marks path of the stage between two points.
A cross represents current position of the stage.
Position of Area of Interest can be changed by pointing mouse cursor over the Area of Interest. Hold down the Ctrl key and the mouse cursor changes its shape to arrows with brown square. Now move the area to a different location. Edit borders of the area to change size or shape of Area of Interest. The status bar on the bottom of the window displays size if the Area of Interest.
Provides overview of the surface used for focusing. It modifies, adds and removes the points, in which the system will refocus. Move the stage to at least 3 different XY positions, focus, and press the  Add Point button each time. The points will determine a plane on which the system will always focus (anywhere on the specimen).
Add Point button each time. The points will determine a plane on which the system will always focus (anywhere on the specimen).
All points used in the focus surface can be redefined using autofocus. Being on the Focus Surface Tab, right-click the (xy) preview and select Auto Focus All Points. Auto focus will be performed and the Z positions modified.
(requires: JOBS Editor) In this tab, the PFS surface created via JOBS is visualized in the form of a heat map. Please see Creating PFS Surface.
Displays an array of XY positions used in currently opened captured ND multipoint document. You can select which point overview is displayed from the pull down menu which offers all available currently opened multipoint documents.
Each tab contains: two upper toolbars with control buttons, an overview area (which can be either graph or data table, depending on which tab is selected in the bottom part of the window), bottom toolbar with controls and arbitrarily Z profile graph area.
Common Controls
 Switch to Area of Interest
Switch to Area of Interest Press this button to hide the whole stage area and display only the Area of Interest.
 Adjust to Points
Adjust to Points Press this button to adjust view so all the points are displayed optimally.
 Full size
Full size Displays the whole stage overview in full range of the view.
 Zoom In
Zoom In Increases magnification of the view.
 Zoom Out
Zoom Out Decreases magnification of the view.
 Show Point Indexes
Show Point Indexes Press this button to display indexes of each point in the overview.
 Show Scale
Show Scale Press this button to display scale in the overview.
 Show Point to Point Distance
Show Point to Point Distance Displays real distance between points in the overview.
 Add Point
Add Point Adds a point at the current position of the stage. You can also use the space bar to add a point.
 Remove Point
Remove Point Removes selected point.
 Remove All Points
Remove All Points Removes all points.
 On Double Click Select Nearest Point
On Double Click Select Nearest Point Double-clicking inside the XYZ Overview area moves the stage. If the button is pressed and you double click near the position where an experimental point is placed, the stage will move precisely to the coordinates defined in the experiment.
 Go to First Point
Go to First Point Moves stage to the first set position.
Note
These commands move the stage to the set position if the Move Stage to Selected Point option is checked. Else the move is done only in the overview window.
 Go to Previous Point
Go to Previous Point Moves stage to the previous set position.
 Go to Next Point
Go to Next Point Moves stage to the next set position.
 Go to Last Point
Go to Last Point Moves stage to the last set position.
 Z Auto Scale
Z Auto Scale Automatically sets scale of the Z axis to provide the best view of the Z profile graph.
 Show Focus Surface
Show Focus Surface Use this button to display Z coordinates of the focus plane in the Z profile graph.
Check this option to make the stage move to the selected point.
Special Controls - ND Acquisition Overview Tab
 Show Scan Areas
Show Scan Areas Use this button to display scan areas. It displays area which matches to single captured image over corresponding point. This area depends on selected Objective or Calibration. If a scan area of one point overlaps some scan areas of different points, or scan area of current stage position (marked with a cross) - the color of those areas is red. If they do not overlap, then it is green.
 Show Image Preview
Show Image Preview Displays/hides the preview image captured around the selected point.
Tip
Right-click over a point and choose a Preview method from the list. Once the specified area is captured around your multi point, adjust your point to sit in a precise position or add more points.
For images with multi-point frames, it is possible to right-click into the image and select Use as preview in XYZ Overview to show the current multi-point in the XYZ Overview or to select Use all XY locations as preview in XYZ Overview and display all multi-points present in the image.
 Show Focus Surface
Show Focus Surface If the focus surface is defined, this button displays its color heat-map. The colors indicate whether the focus surface is tilted or curved. A perfectly horizontal focus surface would be displayed as a solid color.
 Front View
Front View Real position of the sample on the stage is shown in the overview (as seen when standing in front of the microscope).
 Camera View
Camera View Stage overview displays the sample in orientation as it is shown in the live view. Rotation settings in Acquire > Camera Light Path are taken into account.
 Show Z profile
Show Z profile Displays the Z profile graph in the bottom part of the window.
Check this item to keep PFS on while moving between the points.
Special Controls - Focus Surface and PFS Surface tab
 Redefine Z Position
Redefine Z Position Overwrites the currently selected point in the Focus Surface tab with the current Z position of the stage.
 Reload
Reload Each time NIS-Elements application is restarted, the focus surface points are cleared. If you want to use the points from the last session click on this button to reload the points.
Choose the method used for point interpolation. Smooth and Nearest Neighbor methods are available.
If checked, the stage is moved to appropriate coordinates after a point is created.
 Remove All Points
Remove All Points Deletes all PFS surface points.

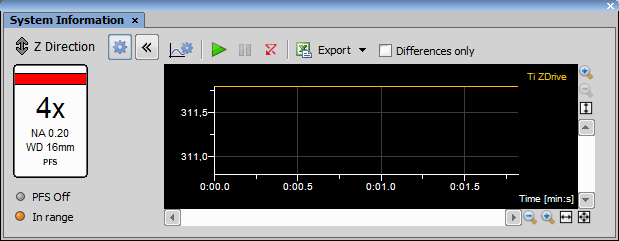
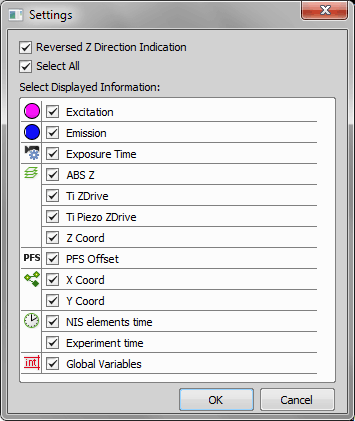
(requires: Z Drive)
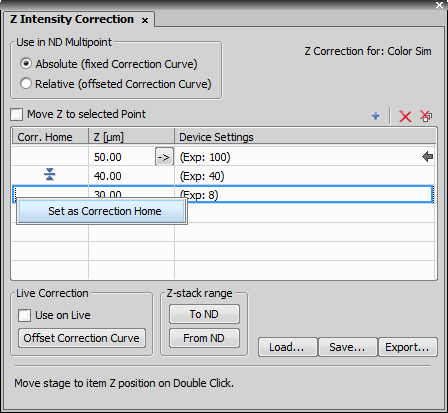
You can define intensity correction for different Z positions using tools in this control window:
Note
The Enable Z Intensity control option must be selected to enable this window. See Appearance Options.
How to define Z intensity correction:
All records are sorted automatically by Z abs value. Z coordinates of defined positions are listed in the second column. The third column displays information about corresponding device settings information, about exposure of a camera, or line setting of a confocal microscope. Use the arrow button between the Z and Device Settings columns to assign current device settings to the selected point.
The white arrow in the corner of the row indicates that the Z coordinate of the selected point is close to the current Z position. The black arrow indicates that the Z coordinate is the same as the current Z position.
Position of the Correction Home is marked in the first column Corr. Home by the  symbol. You can create a home position using the Set as Correction Home command from the contextual menu over the selected point you want to set as the Home position.
symbol. You can create a home position using the Set as Correction Home command from the contextual menu over the selected point you want to set as the Home position.
Select if the Z intensity correction offset is done in absolute or relative coordinates.
Displays information which camera settings is used.
When this option is checked, the NIS-Elements automatically moves to Z coordinate of selected point.
 Add
Add Adds a new Z intensity correction point.
 Remove
Remove Deletes selected Z position from the list.
 Remove All
Remove All Deletes all but Home, Top and Bottom points from the list
Check the Use on live option to perform the Z intensity correction on the live image. After you press the Offset Correction Curve button, a new reference point is assigned to the current Z position and Z coordinates of other points are recalculated to keep the pattern.
The To ND button exports defined points to the ND Z Acquisition. Also it sets the point with the highest Z coordinate as Top and the point with the lowest Z coordinate as Bottom position.
The From ND button imports points (Top, Bottom, Home) from the ND Z Acquisition.
Loads previously saved settings from an external file.
Saves the current settings to an external file.
Exports the list of defined Z positions and Device settings to an Excel sheet.

(requires: Z Drive)
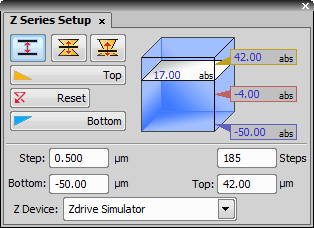
This control window sets the Z drive range.
See Z-series Acquisition for more information about the control tools.

(requires: 2D Deconvolution)
This command displays the Live De-Blur Control Window. Please see Deconvolution > Deconvolution > Show Live De-Blur Setup.

(requires: 2D Deconvolution)
This function displays or hides the Live Denoise & Deconvolution control panel. See Deconvolution > Deconvolution > Live Denoise & Deconvolution.

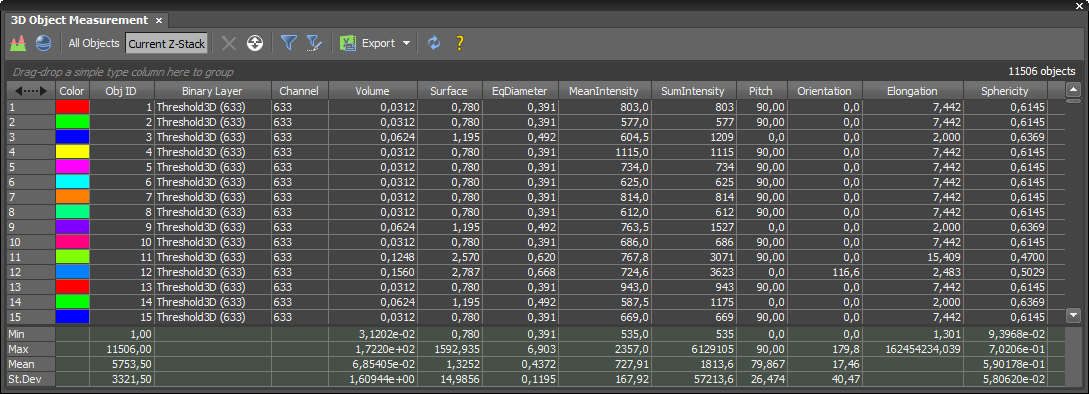
(requires: 3D Measurement)
This window allows you to define the objects for measurement, displays various measurement features and allows you to export the results to Excel.

Analysis Explorer is closely described here: Analysis Explorer.

Opens the results of analyses which were run on the currently opened image. For more information about the Analysis Results panel please see Record Options in Toolbars and Menus.

Manual measurement and annotating of images can be performed using the View > Analysis Controls > Annotations and Measurements  control window. All kinds of measurement and annotation tools are grouped in this window:
control window. All kinds of measurement and annotation tools are grouped in this window:
This toolbar enables you to insert vector objects to the image. The image itself is not affected by the content of the annotation layer, although annotations can be saved with it (JP2, TIFF, and ND2 formats can handle it). After inserting the selected object into the image you can select it using the  Pointing Tool and right-click to edit its Properties.
Pointing Tool and right-click to edit its Properties.
 Confirm with R-Click
Confirm with R-Click If this button is active, each drawn annotation or measurement object has to be confirmed by the secondary mouse click. This is especially useful for adjusting the object's shape and precise placing.
 Switch to Pointing tool after drawing new object
Switch to Pointing tool after drawing new object If turned on, the cursor is automatically switched to the Pointing Tool after drawing an annotation or measurement object.
See the description of all available measurement tools in the Measurement Tools section.
 Appending Labels
Appending Labels Text labels are automatically appended to every new measurement object if this button is turned on. Click the adjacent button to adjust visual properties of the label. The label format can be adjusted in the Manual Measurement section of the Measure > Options window.
Press the Options button to display additional commands:
Select this command to create custom feature. The Measure > Custom Features dialog appears. Press the Add button and define mathematically the feature.
Choose this command to display Measure > Options dialog window.
Loads the previously saved measured data and configuration of their display from an external file.
Saves the measured data and configuration of their display to an external file.
Selects a class number from the combo box next to which is written into the Comment column of the results table. Use this feature e.g. with the  Count tool to count cells (Class 1) and their nuclei (Class 2).
Count tool to count cells (Class 1) and their nuclei (Class 2).
Defines the number of classes. Insert a numeric value.
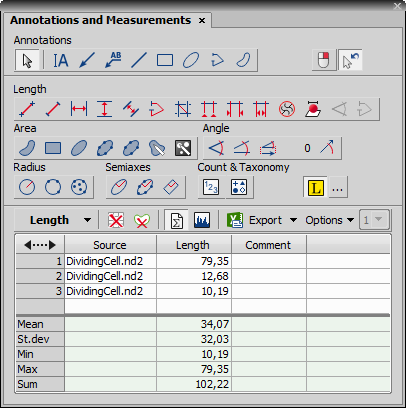
The measured values are being appended to the results table. There is one table for each measurement type. The measured data can be exported to an external file via the standard Export menu (see the Exporting Results chapter for further details).
 Reset Data
Reset Data Pressing this button will erase the currently displayed data, while the data from different types of measurement will not be affected.
 Clear Screen
Clear Screen Removes all measurement objects from the image while the measurement data remain in the results table.
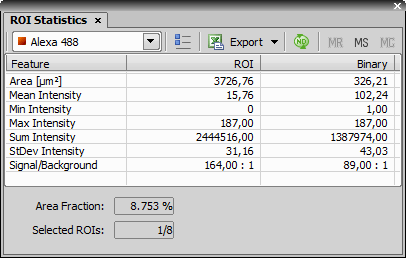
 Statistics
Statistics Click this button to display an additional table where overall statistics (Mean, Standard Deviation, Minimum, Maximum, Sum) of the measured values are displayed.
 Histogram
Histogram Optionally, histogram of the data inside the results table can be displayed by selecting the Show Histogram button.
Measurement results of the currently measured quantity is displayed in the table. Switching between measurement tools of different quantities automatically changes the table contents.
Note
The data remains in the table even after the application is restarted. The data will be erased only after the computer restart.
Contextual Menu Commands
Secondary mouse click in the results table reveals a context menu containing the following commands:
If you have clicked on the Source column, this command enables you to display/hide a full path to the measured image file.
These commands enables you to display any combination of columns that is available for the particular measurement type.
Selecting this command adjusts the column width according to the values it contains.
These commands enable you to adjust the current records selection (made using Ctrl/Shift + mouse) and delete the selected records.
Enables you to select the column to sort the records by, and to remove sorting.
The measurement feature selected in this submenu is displayed in the histogram.
Select units and precision for the display of figures.
 Options
Options The Options button displays a window with options regarding the histogram appearance. Apart from common appearance settings like color, line width, or default text descriptions of the histogram items there are the following options in the window:
In the Mode pull-down menu, you can select the way of displaying the Y axis (number, number in %, cumulative, cumulative in %).
The histogram can be switched to be displayed as a continuous line instead of a number of bars.
Choose a font and its size to be used for describing x and y axes of the histogram. Write your caption of the particular axis into the Caption edit box below.
Select a font and its size to be used when displaying numeral values inside the histogram.
Select the Bins tab in order to adjust the way bins of the histogram are created. If the histogram bins shall be equidistant, bin width, minimum and maximum values can be set. If non-equidistant, each bin limit values should be put inside the definition table.
You can switch between the graph and the table view via these buttons. The histogram source data are displayed in the table view.

The Automated Measurement control window gathers tools needed for fully automated image measurement. The tools can be also displayed as separate panels:
A simple set of tools for binary layers editing. See View > Analysis Controls > Binary Toolbar  .
.
The most common tool for creating a binary layer. See Thresholding.
A tool for classifying pixels. Since it generates a set of binary layers as well as the Thresholding tool does, both these tools are mutually exclusive (only one of them can be selected). See View > Analysis Controls > Pixel Classifier ![]() .
.
For managing of binary layers in the image. See View > Analysis Controls > Binary Layers  .
.
Restrictions applied to the measured binary layers. The purpose of this tool is to exclude the objects which do not match the given criteria from measurement. See View > Analysis Controls > Restrictions 
Classifier of binary layer based on binary object features. See View > Analysis Controls > Object Classifier  .
.
See also Automated Measurement.

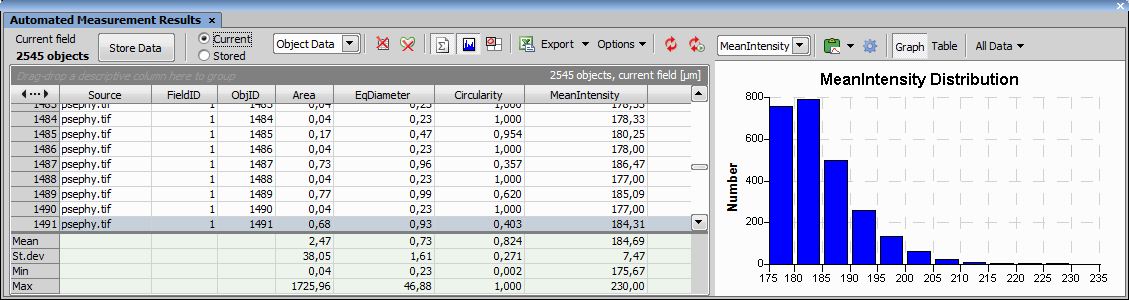
Measured data are displayed within this control window.
Use the following tools to handle the measured data:
This information displays the number of objects in current field.
This button moves the Current data to the Stored repository.
You can select which data repository appear in the table. The Current data are the currently measured data which can be yet modified by changing parameters in the Automated Measurement control window followed by clicking the Update Measurement button. The Stored data cannot be changed. Current data are appended to this repository each time the Store Data button is pressed, or if the Measure > Perform Measurement  command is run.
command is run.
This pull-down menu selects the type of measured data. The selected method updates the entire table and the Graph (histogram) area.
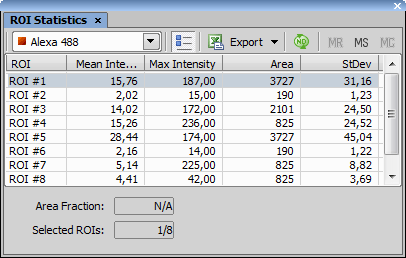
Each row of the table represents object features for a single object.
Table data show mean feature values calculated from all objects present in the selected frame and the selected binary layer.
Lists one field (frame) per table row containing the selected field features.
Lists one ROI per table row each containing statistics of all objects (from all binary layers) inside/touching the particular ROI.
Lists one ROI and binary layer per table row each containing statistics of all objects (from a given binary layer) inside/touching the particular ROI.
 Reset Data
Reset Data This button clears all data.
 Clear Current Measurement
Clear Current Measurement Press this button to clear the current measurement.
 Show Statistics
Show Statistics Press this button to show the statistics.
 Show Histogram
Show Histogram Press this button to show the histogram.
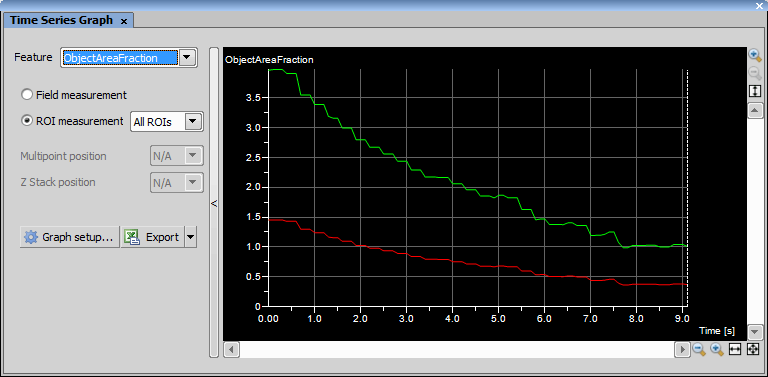
 Time Series Graph
Time Series Graph Press this button to display the Time Series Graph.
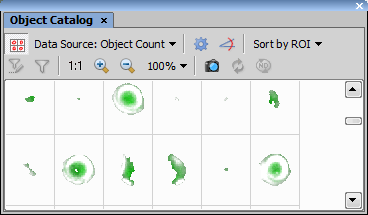
 Show Object Catalog
Show Object Catalog Press this button to display the View > Analysis Controls > Object Catalog  window.
window.
Exports the measured data to various locations. See Exporting Results for more information.
Press the Options button to display additional commands:
Choose which features are measured. See Measurement Features. You can also select the Comment feature which enables user to insert arbitrary comments to measured items in the data area. The length of the comment is limited by 63 characters.
Note
Automatic updating features update the whole result table. If the  Keep Updating or the
Keep Updating or the  Update Measurement feature is used, the content of the Comment column will be removed automatically.
Update Measurement feature is used, the content of the Comment column will be removed automatically.
Choose which features are measured. See Measurement Features. You can select the Comment feature, too (see above).
Choose this command to display Measure > Options dialog window.
Select this command to create custom feature. The Measure > Custom Features dialog appears. Press the Add button and define mathematically the feature.
Loads the previously saved measured data and configuration of their display from an external file.
Saves the measured data and configuration of their display to an external file.
Caution
This command does not save the Current data. To make sure, all data will be saved to a file, click the button beforehand.
 Update Measurement
Update Measurement Press this button to update the current data. Once measurement has been performed, its parameters can be still modified within the View > Analysis Controls > Automated Measurement  panel. This button must be pressed in order for the changes to take effect on the data.
panel. This button must be pressed in order for the changes to take effect on the data.
 Update ND Measurement
Update ND Measurement Press this button to update the current ND document. See ND2 Files Processing.
 Keep Updating
Keep Updating Press this button to keep the data continuously updated.
Data Area
You can arrange the view of images efficiently by grouping them. You can group images according to any feature, or comment. Drag the column name bar to the grouping bar (right above the column name bars). All files with matching field values of the selected column will be grouped together. This can be undone by dragging the column caption back to the others. See Figure 335, “Organizer layout” (the Dimensions column is grouped).
The features are gathered in columns. Click the column caption to sort the data ascending or descending.
The right portion of the window contains data analysis and visualization tools. You can display the histogram of the values or a statistics by pressing the adjacent button. Choose the measurement feature from the pull down menu and its distribution is displayed in the histogram. The data are processed. You can export them to a report, MS Excel application or clipboard. Histogram properties can be changed via the  Options button (see:
Options button (see:  Options). If you have grouped the data, you can also display the histogram of a subgroup. The group can be selected from the Groups menu.
Options). If you have grouped the data, you can also display the histogram of a subgroup. The group can be selected from the Groups menu.
Contextual Menu Commands
Opens a window with a list of measurement features. Select which features you want to measure and press the Add button.
Hides the column you are currently pointing at. To make the column visible again, select it in the Show Column pull down list.
Orders columns by default.
Removes selected entry.
Marks selected entry as invalid data.
Purges records marked as invalid.
Enables the user to select or invert selection of the data.
The data can be sorted according to selected column title in descending or ascending order.
Select a feature you want to inspect in more detail. A histogram (or statistics) of the feature values appears in the right portion of the control window.
Displays the list of all possible units. Select the unit you want to use.
Select the precision of the digits.
(requires: General Analysis)
Opens the Batch GA3 dialog window used for running General Analysis 3 analyses in a batch order. Click on the button and select Content to open a help describing this function.

(requires: General Analysis)
Opens the Batch GA3 Distributed panel used for running General Analysis 3 analyses in a computer cluster. Start by switching to the Settings tab and entering the server name and port on which the NIS-Elements Compute Cluster is running. Then click on  Connect to server. The Dashboard link appears (see below).
Connect to server. The Dashboard link appears (see below).
 Add GA3 batch for distributed processing...
Add GA3 batch for distributed processing... Opens the Batch for distributed processing dialog window where you can choose an existing GA3 recipe from a File or Database in step 1 and then select files which will be processed using the recipe in step 2. Choose the way output files are created from the drop-down menu. The first option uses the edit box to enter the subfolder name whereas the second option sets a file suffix. Preview of the file name and structure is shown below in the Output row. Listed files can be removed using the  Remove selected files from list or
Remove selected files from list or  Remove all files from list buttons.
Remove all files from list buttons.
Note
Make sure that the image being processed is located on a shared storage and not your local hard drive.
 Add folder to be watched...
Add folder to be watched... Opens the Watched folder for distributed processing dialog window used for selecting the recipe (1. Ga3 recipe) and associating it to a specific folder (Folder to be watched). Click to choose a folder which will be used as a “watched folder”. The combo box below specifies the output files location (subfolder/same folder with a suffix) or the overwriting behavior. For more information please see the user manual for NIS-Elements Compute Cluster which should be included in the installation.
 Remove selected tasks
Remove selected tasks Removes the selected task(s).
Opens the NIS-Elements Compute Cluster Dashboard inside your primary web browser. Jobs tab shows an overview of all tasks sent to the cluster (computer network) to be processes. Currently the following processing types are supported: AI Training, Batch Deconvolution, Batch Ga3 Distributed. Nodes tab shows all computers involved in the processing. Please see the NIS-Elements Compute Cluster Manual for more information.
 Disconnect from server
Disconnect from server Click on this button if you need to disconnect your computer from the server. Dashboard link disappears and “Disconnected” is shown.
This tab shows all unfinished tasks. “Running” and percentage progress is displayed. The number of pending tasks is shown in the bracket.
This tab shows all finished tasks. Double-click on a finished task to open the image. To see the Task Output log, choose Show log... in the context menu over an image file.
The number of processed tasks is shown in the bracket.
This tab shows all computers involved in the processing. The number of nodes is shown in the bracket.
This tab sets the server name and port for the NIS-Elements Compute Cluster.

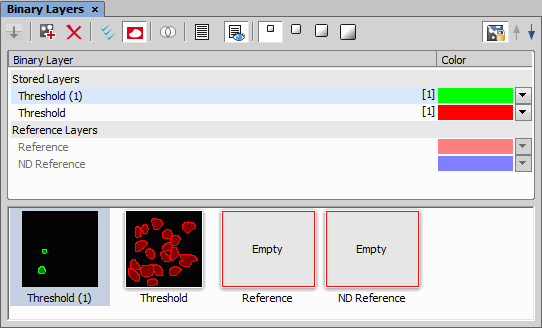
Number of binary layers can be present. A new binary layer can be created for example in the Binary > Binary Editor. Manage the binary layers using the View > Analysis Controls > Binary Layers  control window:
control window:
 Store Selected Working Layers
Store Selected Working Layers Moves the selected Working Layers to Stored Layers
 Duplicate Selected Layers
Duplicate Selected Layers Duplicates selected binary layers.
 Remove Selected Layers
Remove Selected Layers Removes selected binary layers.
 Select All Layers
Select All Layers Marks all working and stored layers in the list.
 Show Reference Layers
Show Reference Layers Displays/hides reference layers in the list.
 Binary Operations Dialog
Binary Operations Dialog Opens the Binary Operation dialog window.
 Show Layer List
Show Layer List Displays a list of binary layers. Maximally 9 items are displayed.
 Show Thumbnails
Show Thumbnails Displays a list of binary layers thumbnails. Maximally 10 thumbnails are displayed.
 Show List and Thumbnails
Show List and Thumbnails Displays both lists - list of binary layers and thumbnails.
 Connect objects to 3D
Connect objects to 3D Creates 3D objects for selected binary layers.
 Fill missing binary frames
Fill missing binary frames Copies binary layer from the current frame to all frames where binary layer is missing. Apply this function on currently opened ND document if it contains more than one frame and the binary layers are not defined for all frames.
 Thumbnail size
Thumbnail size Sets size (small, medium, big, extra big) of displayed thumbnails.
Contextual Menu Commands
When you right click a thumbnail or binary layer name, a contextual menu appears with additional commands:
This command selects all binary layers.
This command copies selected binary layer to clipboard.
This command pastes copied binary layer.
Name of currently active binary layer is displayed.
This command removes selected binary layer.
This command renames selected binary layer.
This command duplicates selected binary layer.
This command clears selected binary layer from document.
Color of the binary layer can be changed from this color pull down menu.
Uses a smart algorithm to prevent neighboring objects to have similar color.
Colorizes objects by 12 different colors in the direction from the top left corner to the bottom right corner.
It is possible to colorize objects according to a measured value (such as Area) using the General Analysis 3 module. Then it can be displayed by this option.
This command opens list of components to which the selected binary layer can be attached.
This command detaches selected binary layer from the component back to all components of the document.

The most frequently utilized binary tools are grouped in the Binary Toolbar control window. Run the View > Analysis Controls > Binary Toolbar  command to display it. It contains the following tools:
command to display it. It contains the following tools:
 Pointing tool
Pointing tool This tool turns the mouse cursor to a pointing tool.
 Auto Detect
Auto Detect Click in the middle of an object and the system will try to detect its borders and highlight them. The algorithm is based on changes of intensity values. The object size can be adjusted by mouse wheel or by the UP/DOWN keys. Finish the detection by right click.
 Auto Detect All
Auto Detect All Click in the middle of an object and drag the mouse to its borders. The system tries to detect the object borders as well as find all the other similar objects. Finish the detection by releasing the mouse button.
 Draw Object
Draw Object Draw a binary objects by hand. You can either draw it like polygon or use the “freehand” method while holding the primary mouse button pressed.
 Delete Object
Delete Object Click inside a binary object which you would like to delete.
 Separate Objects Manually
Separate Objects Manually Press the primary mouse button and drag it between two connected objects in order to separate them with this tool.
The following tools perform basic morphology operations. Please refer to the Mathematical Morphology Basics chapter for further details. The Reset Binary tool erases the current binary layer.
 Dilate
Dilate  Erode
Erode  Close
Close  Open
Open  Separate Objects Automatically
Separate Objects Automatically  Clean
Clean  Fill Holes
Fill Holes  Clear
Clear Erases all binary objects

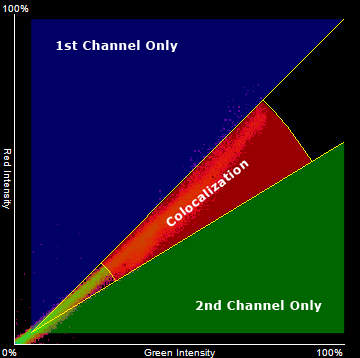
Colocalization characterizes the degree of overlap between two different fluorescent labels, each having a separate emission wavelength. Practically it displays graphical representation of the intensity distribution of two channels. This is helpful while segmenting images. Also colocalization reports statistical information about the entire image, or a ROI, respectively. NIS-Elements estimates colocalization by calculating several colocalization coefficients. The colocalization is represented by a scattergram.
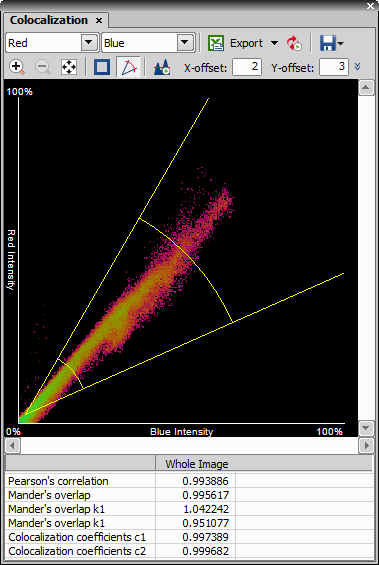
The scattergram indicates a degree of coincidence of overlapping pixels. All possible combinations of pixel intensities of the selected color channels are displayed within the scattergram. Intensity of each point in the scattergram is proportional to the number of pixels with the corresponding intensity combination (purple = low accumulation of the particular intensity combination, green = high accumulation).
Colocalization tools
Choose the two channels from the pull down menus.
The colocalization coefficients can be exported out of NIS-Elements. Please, refer to the Exporting Results chapter.
 Keep Updating Binary
Keep Updating Binary If turned ON, the binary layer is updated during some user actions such as browsing through an ND2 document.
 Open/Save Colocalization Settings
Open/Save Colocalization Settings Saves / loads the colocalization settings under a user defined name.
 Zoom In
Zoom In Zooms in the scattergram. The zoom size is indicated at the end of both axes.
 Zoom Out
Zoom Out Zooms out the scattergram. The zoom size is indicated at the end of both axes.
 Graph Autoscale
Graph Autoscale If zoomed in, this button returns the scattergram zoom back to 100%.
 Rectangular selection
Rectangular selection A binary layer will be created over pixels of the image with values that fit the rectangular area of the scattergram.
 Sector selection
Sector selection Works in the same way as the rectangular selection. Move the yellow radius line and adjust the concentric circles to delimit the area of interest. X and Y offset of the whole sector can be set in the edit boxes on the right side.
 Threshold on Pearson's correlation
Threshold on Pearson's correlation This tool highlights the pixels which fit the defined degree of correlation. The percentage threshold can be set in the edit box which appears when you activate the tool.
 More buttons
More buttons Reveals more buttons of the Colocalization window.
Three binary layers are created in the source image. One binary layer represents the colocalized area defined by the yellow radius lines and concentric circles (red area in the picture below) and two layers represent the rest of the channel intensity combinations available (blue and green areas in the picture below).
Statistic tools
Image statistics is displayed at the bottom part of the control window.
This value indicates an overlap of two channels. It is independent from the image background.
This value indicates an overlap of two channels - it is not dependent on the relative strengths of the channels, but depends on the background.
The coefficients k1 and k2 describe intensity variations between channel 1 and channel 2. Values depend on the intensities of two channels. They are sensitive to the difference in the channel intensities.
The coefficients c1 and c2 (often documented as M1 and M2) describe contribution of each channel to the overall colocalization. Values are not sensitive to channel intensities. They can be used when the numbers of objects are not equal.

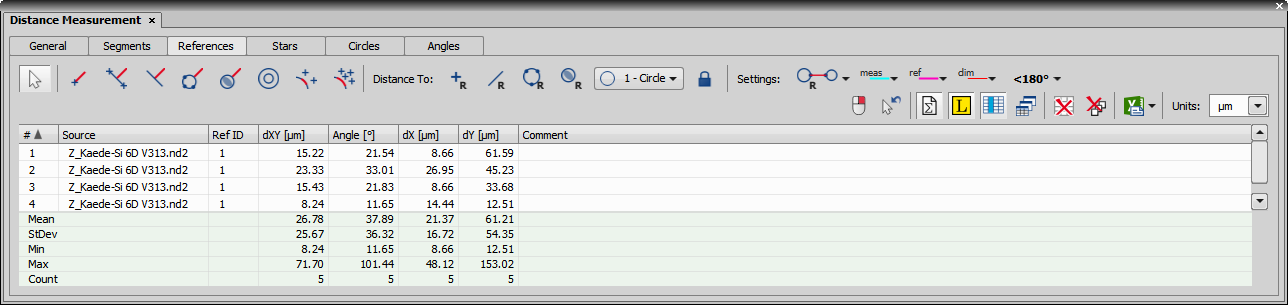
Distance Measurement panel provides a full set of measurement tools arranged into six main groups (tabs). Each tab holds the results for each measurement group.
The table below the measurement tools shows the measurement results and statistics based on the settings of the tools on the right side of the panel. Context menu over a table header enables the user to select which label is shown in the image next to the measurement (Show Source on Label) and to set the Columns Visibility (see below). Context menu over the results data enables the user to Deselect All Rows, Remove Selected Rows, Resize Columns to Contents, Resize Columns to Defaults and Resize Columns Relatively.
Common Tools
 Pointing Tool
Pointing Tool Basic tool for selecting objects in the image.
 Results by Reference
Results by Reference If this button is pushed, only the results linked to the selected reference object are shown. If the button is not pushed, all reference measurements linked to all reference objects are shown.
These drop-down menus are used to change the color and size of the measurement objects, reference objects and dimension lines. In the References and Stars tab, points of interest can be further specified.
 Confirm on Right Click
Confirm on Right Click Confirms the drawing of a measurement object by the secondary mouse click.
 Switch to Pointing Tool After Drawing
Switch to Pointing Tool After Drawing Automatically switches to the pointing tool after drawing a measurement object.
 Show/Hide Statistics
Show/Hide Statistics Shows/hides the statistics area at the bottom of the measurement table.
 Show/Hide Labels
Show/Hide Labels Shows/hides the measurement labels.
 Columns Visibility...
Columns Visibility... Opens the Columns Visibility dialog where it is possible to select which measurement features are shown as columns. The same dialog can be opened from the context menu over the results header.
 Show Results from All Documents/Show Results from the Current Document
Show Results from All Documents/Show Results from the Current Document Displays the measurement results either from all images or just the current image.
 Delete Measurement
Delete Measurement Deletes all measurements from the currently selected tab.
 Delete All Measurements
Delete All Measurements Deletes all measurements from all the measurement tabs.
 Export to Excel
Export to Excel Drop-down menu next to this button selects whether to export the measurement data and statistics to Excel, to a File or to Clipboard and whether all measurement tabs are exported as separate excel tabs (All Tabs) or just All Visible Columns are exported. Once the selection from the drop-down menu is made, click this button to perform the actual export.
Defines the measurement units.
General
 2 Points
2 Points Draws a line defined by two points (shown as crosses).
 Simple Line
Simple Line Draws a simple line.
 Vertical Lines
Vertical Lines Draws two parallel vertical lines.
 Horizontal Lines
Horizontal Lines Draws two parallel horizontal lines.
 Free Parallel Lines
Free Parallel Lines Draws two parallel lines with a free rotation. Draw the first line, confirm it by a secondary mouse click and repeat this procedure for the second line.
 Crosses
Crosses Draws a line defined by two points which are highlighted by crosses over the whole image.
 3 Points Arc
3 Points Arc Draws an arc by clicking 3 points on it. The second point defines the direction and the third point defines the diameter dynamically during its placing.
 3 Points Circle
3 Points Circle Draws a circle by clicking 3 points on it.
 Circle
Circle Draws a circle by clicking and dragging.
 Autodetect Circle
Autodetect Circle Automatically detects a circle with its center in the center of gravity of the clicked object (confirm its detection by the secondary mouse click). The circle has the same area as the detected object.
 2 Points with XYZ Stage
2 Points with XYZ Stage This function is used for measuring the distance between two points going outside the field of view. Run the live image, click a point in the image, move your stage and click in the image again. The line between the two clicked points is measured.
 Crosses with XYZ Stage
Crosses with XYZ Stage This function is used for measuring the distance outside the field of view with auxiliary crosses. Run the live image, move the first cross to your point of interest and confirm its position by the secondary mouse click. Move your stage and repeat the procedure for the second point. The distance between the two points is measured.
Note
If an XY/Z stage is connected, coordinates of its current position are shown on the right side of the Distance Measurement panel.
Segments
 Define Segments by Polyline
Define Segments by Polyline Draw a polyline by clicking into the image and confirm it by the secondary mouse click. The segments defined by the nodes are automatically separated and numbered in the results table. Secondary-mouse click on the header of the measured feature and select Show ... on Label to label each segment in the image with its measured value.
References
To measure reference distances, a reference object has to be defined first. Start with a reference tool from the Distance To toolbox. If multiple reference objects are defined, select one from the drop-down menu next to the reference tools. Then choose which distance is to be measured from the measurement tools on the left.
 Point Distance
Point Distance Measures the distance between the reference object and this defined point.
 2 Point Line Distance
2 Point Line Distance Draws a line with two points. The orthogonal distance between this line and the reference object is measured.
 Simple Line Distance
Simple Line Distance Draws a simple line. The orthogonal distance between this line and the reference object is measured.
 Linear Pitch
Linear Pitch Measures the distance between two drawn parallel lines which are orthogonal to the reference line.
 Linear Continuous Pitch
Linear Continuous Pitch Measures the distances between multiple clicked parallel lines which are orthogonal to the reference line.
 3 Points Circle Distance
3 Points Circle Distance Draws a circle by 3 points and measures the distance between the circle center and the reference object.
 Auto Detect - Circle Distance
Auto Detect - Circle Distance Automatically detects a circle with its center in the center of gravity of the clicked object (confirm its detection by the secondary mouse click). The circle has the same area as the detected object. Distance and angle between the circle center and the reference object is measured.
 Concentric Circle
Concentric Circle Draws a concentric circle with the reference object as its center and measures the distance features between them.
 Circular Arch
Circular Arch Draws two points which define the arc on the reference circle which is measured.
 Circular Continuous Arch
Circular Continuous Arch Draws multiple points which define the arch segments on the reference circle which are measured.
 Define Reference Point
Define Reference Point Defines the reference as a single point.
 Define Reference Line
Define Reference Line Defines the reference as a simple line.
 Define Reference Circle
Define Reference Circle Defines the reference as a circle set by three points.
 Define Reference Circle - Auto Detect
Define Reference Circle - Auto Detect Defines the reference as a circle detected automatically around the selected object. Click on a visible object and confirm its detection by the secondary mouse click.
Stars
This type of measurement is used to measure reference distances and angles of objects around one reference object which has to be defined first. Start with a reference tool in the Distance To toolbox. If multiple reference objects are defined, select one from the drop-down menu next to the reference tools and choose which distance is to be measured from the measurement tools on the left.
 Point Distance
Point Distance Measures the distance and angle between the reference object and this defined point.
 3 Points Circle Distance
3 Points Circle Distance Draws a circle by 3 points and measures the distance and angle between the circle center and the reference object.
 Auto Detect - Circle Distance
Auto Detect - Circle Distance Automatically detects a circle with its center in the center of gravity of the clicked object (confirm its detection by the secondary mouse click). The circle has the same area as the detected object. Distance and angle between the circle center and the reference object is measured.
 Concentric Circle
Concentric Circle Draws a concentric circle with the reference object as its center and measures the distance features between them.
More measurement features can be added from the context menu over the table header (Columns Visibility), such as Cref-C (distance between the center of the reference circle and the center of the second circle) or Cref-E (distance between the center of the reference circle and the edge of the second circle).
 Define Reference Point
Define Reference Point Defines the reference as a single point.
 Define Reference Circle
Define Reference Circle Defines the reference as a circle set by three points.
 Define Reference Circle - Auto Detect
Define Reference Circle - Auto Detect Defines the reference as a circle detected automatically around the selected object. Click on a visible object and confirm its detection by the secondary mouse click.
Circles
 3 Points Circle Distance
3 Points Circle Distance Draws a circle by 3 points and measures the distance and angle between the circle center and the reference object.
 Auto Detect - Circle Distance
Auto Detect - Circle Distance Automatically detects a circle with its center in the center of gravity of the clicked object (confirm its detection by the secondary mouse click). The circle has the same area as the detected object. Distance and angle between the circle center and the reference object is measured.
 Concentric Circle
Concentric Circle Draws a concentric circle with the reference object as its center and measures the distance features between them.
 Define Reference Circle
Define Reference Circle Defines the reference as a circle set by three points.
 Define Reference Circle - Auto Detect
Define Reference Circle - Auto Detect Defines the reference as a circle detected automatically around the selected object. Click on a visible object and confirm its detection by the secondary mouse click.
Angles
 Angle
Angle Draws two connected lines and the angle between them is measured.
 Angle between Lines
Angle between Lines Draws two separated lines and the angle between them is measured.
 3 Points Angle
3 Points Angle Draws two lines defined by clicking three points and measures the angle between them.
 4 Points Angle
4 Points Angle Draws two lines defined by clicking four points and measures the angle between them.
 Angle To Reference Line
Angle To Reference Line Draws a line and measures the angle between this line and the previously drawn Reference Line.
 Define Reference Line
Define Reference Line Defines the reference as a simple line. Set the reference line from the drop-down menu.
Sets a range in which the angles are measured.

(requires: EDF Module)
The EDF module is needed to display the Z profile
This control window displays and measures a Z profile of a focused image which was produced by the EDF module.
There are three tabs at the bottom of the Z Profile control window named Graph, Data, and Measurement. Switch from the default Graph tab to the Data tab. The number, X, Y, and Z coordinates of every point of the Z profile is displayed there in a table. They can be exported using the Export button described below.
Some measurement actions can be performed within the graph. The results are written to the Measurement tab.
Tools
 Hide/Show profile
Hide/Show profile This button displays/hides the profile line inside the image window. The profile line can be dragged by mouse and the length can be modified. In the 3D Surface view mode (click  Show EDF 3D Surface View button on the image toolbar) the EDF Z-Profile plane can be moved by clicking Ctrl and dragging with the left mouse button.
Show EDF 3D Surface View button on the image toolbar) the EDF Z-Profile plane can be moved by clicking Ctrl and dragging with the left mouse button.
 Z-Profile Options
Z-Profile Options The appearance and behaviour of the graph can be modified in the Z-Profile Options window. Press this  button to display it or click the General Profile Properties... from the context menu over a profile line.
button to display it or click the General Profile Properties... from the context menu over a profile line.
 Export
Export Click this button to display a pull-down menu. The Graph image, graph data, and the measurement results can be exported:
The data and measurement tables can be exported to MS Excel. A new XLS sheet opens and the table is copied to it automatically. There is also the Export All To Excel option, which copies the data table, measurement table, and the graph image into it.
The data and measurement tables can be exported to an external *.txt file, the graph image to a *.bmp file. Select the command from the pull-down menu and define the target file name in a standard Save As-like window, which opens. Confirm the export by the Save button.
The data table, measurement table, and the graph image can be exported (copied) to Windows clipboard. Then the data or the image can be inserted into any appropriate application (text editor, spreadsheet processor, graphics editor) typically by the Paste command.
The Graph image can be exported into the Report Generator (see: Creating Reports).
The following interactive measurements can be performed within the graph. Please see the details in the Measurement on Graph chapter.
Note
Be aware that the scale in the X axis and the Y axis directions usually differ. In such case, the measured value does not match the angle displayed on the screen.
 Distance from Baseline
Distance from Baseline Use this function to draw a red reference line (base line) by clicking and dragging in the graph area. Then click any other point(s) in the graph to measure its orthogonal distance to the base line. Finish the measurement by the secondary mouse click.
 Clear Measurement Objects
Clear Measurement Objects Deletes all the measured objects in the graph.
 Reset Data
Reset Data Clears the table with the measurement results.
 Show Measurements
Show Measurements Use this button to show a table containing results of measurements made in the graph.

 Shift Profile Line
Shift Profile Line Enter the shifting step into the edit box (units are taken from the current image) and click on one of the arrows to move the profile line in the X axis.
 Show 1:1 Axis Ratio
Show 1:1 Axis Ratio Sets the axis ratio of the graph to 1:1 so that both axes have the same calibration.
The Z-profile graph may be zoomed in the usual way. You can click the zoom buttons placed on the control window sides (please see the Image Window chapter for the buttons description) or a mouse wheel can be used:
Point to the target area and roll the mouse wheel. The graph will be zoomed in/out according to mouse wheel movement direction.
Zoom while holding the Ctrl key down.
Zoom while holding the Shift key down.
EDF Z-profile Options  Click the Options button. A dialog appears where you can specify the Z- profile options:
Click the Options button. A dialog appears where you can specify the Z- profile options:
General Options tab
Choose background, axes and grid colors from the palette. Check the Graph Title option to display a title, whose text you can enter in the adjacent field. Then check the Show Horizontal/Vertical Grid items if you want to make them visible in the graph. If X/Y Axis Always Visible item is checked, the axes do not leave the graph area while zooming in the graph.
Select interpolation method or drawing the graph lines by pressing the relevant button. You can choose Steps (rough), Linear (smoother), or Bicubic (really smooth) interpolation method.
Check this item to display data points. Small dots indicating the actual data values position can be displayed on the graph line. The points appear only if the distance between them is big enough for them to be recognized (they usually appear when you zoom in the graph).
Turning this option ON will make the graph lines look smooth.
Check this item to fill in the area under the line chart with a color. Select the amount of opacity used from the list of predefined values.
Defines the color and width of the profile line.
If this option is checked, the new graph measurement always overwrites the old one. If the function is not checked, measurement history remains in the graph.
X axis
The Auto option enables that the range values are set automatically. On the contrary the range values can be set on Fixed values also. The range values can be set for minimum of X axis, maximum of X axis, major and minor grid of X axis.
If you select the Best Fit option, zoom of the X axis will be set to best fit. Otherwise you can set the Fixed range.
Y axis left
The Graph Range and Zoom options are described above.
Set the line appearance - line color (in case color of image component is not set), thickness and style (solid, dot, dashed, dash-dot).

Please see General Analysis 3 .

Shows the GA3 Results - Main panel with results specified in the Results & Graphs > Layout > Display node.

Shows the GA3 Results - Side panel with results specified in the Results & Graphs > Layout > Display node.

This control window displays the image intensity profile.
See Measure > Intensity Profile  for more information.
for more information.

(requires: JOBS Editor)
This control window is used for managing jobs. The following control window appears:
See Introduction to Jobs Explorer for detailed description of this window.

(requires: JOBS Editor)
A job can be added to the toolbar from within the View > Analysis Controls > JOBS Explorer  window - just right click on the job name and select Show on Toolbar. The job appears in the JOBS Toolbar:
window - just right click on the job name and select Show on Toolbar. The job appears in the JOBS Toolbar:
This control window enables the user to easily edit the contained jobs, run the jobs or job wizards.

(requires: Local Option)
Displays the Layer Thickness Measurement window. See Layer Thickness Measurement.

(requires: Local Option)
Opens the Measurement Explorer panel.
See also Measurement Explorer.

(requires: Local Option)
Opens the Measurement Sequencer - Definition panel used for the preparation of advanced sequential measurement definitions.

(requires: Local Option)
Opens the Measurement Sequencer - Run panel used for executing the measurement definitions previously defined in the View > Analysis Controls > Measurement Sequencer - Definition  window.
window.

(requires: N-STORM Analysis)
Opens the Molecule Analysis dialog window used for localizing molecules.
For more information, please see Molecule Analysis.

(requires: NIS.ai)
Opens the NIS.ai Explorer, please see NIS.ai Explorer for more information.

This control window displays the objects present in the analyzed imaged. The Object Catalog is filled with objects at the measurement. The objects can be filtered and sorted. In the contextual menu are additional commands which enable object validation. If you place the mouse cursor over the image thumbnail, a window appears displaying the info about the object measured features.
Top Toolbar
Press this  button to fill the Object Catalog with data from Automated Measurement Results.
button to fill the Object Catalog with data from Automated Measurement Results.
Choose the data source. Either the Object Count or the Automated Measurement data source is automatically set according to from which window was the Object Catalog invoked.
Press this  button to change the Object Catalog Settings.
button to change the Object Catalog Settings.
Press this  button to adjust automatically orientation of all objects.
button to adjust automatically orientation of all objects.
Select the sorting features (Feature of Interest, Ascending or Descending sort) from the pull down menu that appears after you press this item. The Feature of Interest item is available only for option Unsorted. It displays by which feature the objects are sorted.
Press this  button to define the filter. This button opens the Define Filter window.
button to define the filter. This button opens the Define Filter window.
Select a feature from the list of relevant features in the pull down menu and set the range values.
Note
When using the results from Object Count, the filtering options in Object Catalog are unavailable.
Press this  button to apply the filter set in the Define Filter window. To discard the filtering conditions, press this button once again. When filtering is active, the icon is highlighted red.
button to apply the filter set in the Define Filter window. To discard the filtering conditions, press this button once again. When filtering is active, the icon is highlighted red.
Note
When using the results from Object Count, the filtering options in Object Catalog are unavailable.
Edit the style of viewing the thumbnails.
Check this option to set the same zoom for all thumbnails.
Choose the thumbnail size: Icons, Small, Medium, or Large.
Press this  button to create a snapshot of all object in Object Catalog. A new image is created.
button to create a snapshot of all object in Object Catalog. A new image is created.
Press this  button to update object catalog.
button to update object catalog.
Contextual Menu
Deletes selected objects.
Deletes all records in the Object Catalog.
Invalidates/validates selected objects.
Deletes invalid objects.
Move stage to object position.
Object Catalog Options
This window displays the Object Catalog setting.
Choose this option to let the thumbnails size reflect the size of objects. Define size of the border in micrometers.
Choose this option to display the thumbnails in rectangles with fixed size. Define the rectangle dimensions in micrometers.
Check this option to hide surroundings of the objects.
Check this option to draw the contours of object.
Check this option to display the binary overlay in the thumbnail image.
If you check this option, the objects will have unique overlay color for each measured field.
Check this option to show the feature value of object in left top corner of thumbnail.
This option makes the objects in the catalog comparable by size.
Check this option to show the thumbnails in regular square grid.
Check this option to draw grid lines between thumbnails.

(requires: Object Classifier)
This command opens the object classifier window. See Object Classifier.

The Object Count tool thresholds the image, automatically measures the binary objects, and exports the measured data to a file in a straightforward way.
See Object Count for detailed functionality description.
This control window displays the Pixel Classifier. Pixels can be classified according to selected features:
Specify the number of phases by pressing  and
and  buttons. Finish the definition by clicking
buttons. Finish the definition by clicking ![]() Define again.
Define again.
Control Window Options - the Training Mode
This button switches between the standard and the training mode of the classifier. Click ![]() Define to start training the classifier.
Define to start training the classifier.
These buttons are available only in the training mode. Use one of these buttons  ,
,  ,
,  and click into the image to select pixel(s) which will be used as samples for the current class.
and click into the image to select pixel(s) which will be used as samples for the current class.
 Reset samples
Reset samples Press this button to delete all samples from the current class.

 Undo/Redo
Undo/Redo Standard Undo and Redo commands.
 Smooth
Smooth This command applies smooth operation on the classified objects. Choose the smooth strength from the pull-down menu next to the button.
 Show Scattergram
Show Scattergram This button displays the scattergram.
 Keep Updating Classifier
Keep Updating Classifier Press this button to run the classification continuously. Any changes in the image influencing the classification are shown immediately.
 Classify in ROI On/Off
Classify in ROI On/Off Press this button to determine if pixel classification is done only in ROIs (Classify in ROI On) or in the whole image (Classify in ROI Off).
Select a classification method of evaluating the binary objects. Manual enables defining the classes manually. If Bayes is selected, classes are defined via an algorithm for calculating classes from the defined samples. Neutral Network defines the classes via neutral network algorithm from the defined samples.
Select which data are used for classification: Intensity; Channels; Hue, Saturation, Intensity (for RGB images); or Ratio from the picker. Then specify further details picking the appropriate item from the Channels menu.
This window contains list of all defined classes. When in the training mode, you can change the name or the displayed color of each class. If you check the Background option, the selected class is set as background. The Area values define size of the selected class area in proportion to the whole image and also in document units. Press the  Test button to display classified objects in the image. Check the Show All option to display all classes in the image. If you do not check this option, only the currently selected class is displayed.
Test button to display classified objects in the image. Check the Show All option to display all classes in the image. If you do not check this option, only the currently selected class is displayed.
The slider on the left side defines scale of the histogram in the definition area. To define classes, drag the borders between them or set the value manually in the field which appears when you move your mouse cursor near the border line.
Control Window Options - Standard Mode
 Update Classification
Update Classification Runs classification on the current image.
 Classify ND image
Classify ND image Runs classification on the whole ND2 file.
 Store classified data
Store classified data Saves current data from the classifier section into the stored data section.
 Export
Export Exports the data to a file, MS Excel or clipboard.
 Open / Save classifier
Open / Save classifier Stores and imports the classifier settings.
This table contains all stored data.
 Show Area Fraction button converts the stored data into the proportion of the total area [%].
Show Area Fraction button converts the stored data into the proportion of the total area [%].
You can use the Remove Data  button to remove the current row or the Remove All Data
button to remove the current row or the Remove All Data  button to remove all data present in the table.
button to remove all data present in the table.
Pixel Classifier Scattergram
Scattergram window appears after clicking  Show scattergram. Select two features which will be jointly represented in the graph. Press the
Show scattergram. Select two features which will be jointly represented in the graph. Press the  Show Grid button to display the grid. Press the
Show Grid button to display the grid. Press the  button to display options defining the graph appearance.
button to display options defining the graph appearance.

This panel applies limits to objects in the measurement results table. Only objects which fit these limits will remain in the table.
How to Set Restrictions
 Reset
Reset Resets all restrictions to to default values.
 Generate Binary Using Restrictions
Generate Binary Using Restrictions Creates new binary layer using the set restrictions.
 Select Object Features
Select Object Features Selects the measurement features. The Measure > Object Features dialog box appears.

This control window displays information about the current Measurement ROI (region of interest).
The following information of the image and the binary layer is available. The statistics include information about the whole image or just the parts covered with Measurement ROI depending on whether the ROI is ON or OFF. The channel can be selected from the combo box.
Displays standard deviation of the intensity values
Displays the signal / background ratio, tha Signal value is calculated as follows:
The function takes 0.1% of the brightest and darkest pixels and only the highest frequency (modus) is used as the MaxInt and MinInt values.
Note
You can modify the quantile size in the Windows Registry Editor under HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Laboratory Imaging\Platform\User.Name\Platform.INI\Configuration\ROIStatistics.HundredthOfPercent - the default value is 10 (10 x 0.01% = 0.1%).
Other options
 Multiple ROI mode
Multiple ROI mode This button switches the ROI statistics window into the Multiple ROI mode displaying summary results per each ROI.
The displayed data can be exported to a text or MS Excel file via a standard Export pull-down menu. Please see the Exporting Results chapter for further details. If an ND2 file is opened, this  button performs the export of ROI statistics of all its frames according to the defined settings. You will be Navigation in ND2 Files.
button performs the export of ROI statistics of all its frames according to the defined settings. You will be Navigation in ND2 Files.
This functionality easily compares different ROI statistical data.

Shows memorized data.

Memorizes current data.

Clears memorized data.
This control window provides thresholding tools.
See Thresholding for more information.

Records the average pixel intensities within ROIs during a time interval.
See Time Measurement for detailed description of this control window.

This control window allows you to generate graphs describing various features of the image in time. When having an image with Z-stacks, it is possible to choose between the Z-stack positions.
The features can be chosen in the View > Analysis Controls > Automated Measurement Results  window in the Options tab - Select Object / Field and ROI Custom features.
window in the Options tab - Select Object / Field and ROI Custom features.
The features can be measured either in the Field or in the ROI area only.
More information on Features in the section Measurement Features.
The measurements are generated from the whole area of the image. You need to create a binary layer to be able to perform field measurement.
All ROIs - the measurements are generated from all the ROIs in the image. The binary layer is not necessary.
ROI number - the measurements are generated only for the specific ROI.
When having an image with a multipoint dimension, you can choose the specific position for the measurements.
You can choose the specific Z-stack position for the measurement, if contained in the image.
This tab offers you the options to change the graph setup.
Graph options
X axis
Y axis left
This option allows you to export the resulting graph to Excel, Clipboard, Raster file or Report. See Exporting Results.
(requires: Object tracking)
Motion characteristics of objects such as living cells can be measured automatically or manually using the Tracking control window.
See Tracking for more information.
(requires: Object tracking)
Options for proper tracking of objects can be set in the Tracking Options control window.
See Tracking Options for more information.

Measures the volume of an object.
Select a channel from the list of all channels present in the current image. Press the Measure Volume to start the current position measurement. The data can be exported via the Export button to external file or to the MS Excel application. When you press the Reset  button, all data will be removed. If you want to measure all Z-stacks, check the check box next to the Reset button.
button, all data will be removed. If you want to measure all Z-stacks, check the check box next to the Reset button.
After the position is measured, the data appear in the table below.

(requires: Measurement Sequencer)
Opens the Weld Measurement dialog window. See Weld Measurement.

Manages the visibility of all control windows.
The main portion of the window contains controls overview. All controls displayed in the application top toolbar are displayed here. You can add another control using the Customize button.
Pressing a control button results in displaying (or hiding already displayed) control window within the application layout.
Control Window Options
 Show Groups
Show Groups Press this button to sort the controls displayed in the control window to groups (Acquisition Controls, Analysis Controls, ...). These groups can be expanded or collapsed by the +/- buttons. Items in each group are displayed in alphabetical order.
 Show Bitmaps
Show Bitmaps Press this button to display the controls represented by their icon only.
 Show Text
Show Text Press this button to display the controls represented by their name only.
Press the Customize button to expand a menu containing all available control window sorted in four submenus. When you select any control from the submenu, the control is added to the control window overview portion and to the application top toolbar as well. The Add All Controls command adds all available controls to the overview and application toolbar at once. Similarly the Remove All Controls command removes all controls.
 Associate with Current Layout
Associate with Current Layout When this button is pushed, different contents of the control panel are saved for each layout.
Right-clicking on the buttons in the top application toolbar displays a context menu with the Remove This Button command enabling to remove the button from the toolbar.
This control window displays a histogram.
See Histogram for detailed window description.

This command shows the LUTs control docking window. Look-up tables are used for image color and brightness modifications.
See detailed description of LUTs functionality and control in the LUTs - Non-destructive Image Enhancement chapter.

Opens the Molecules Options dialog window used for visualizing molecule images (ND2 files containing the molecule data format). This window can also be opened from the image window (Image Window ) after clicking the  View Molecules button.
View Molecules button.
For more information, please see Molecule Options.

This control window displays previews of all opened documents.
You can customize display of image thumbnails. Use the buttons to change size of the thumbnail images. Thumbnails can be lined up in a single row  or in multiple rows
or in multiple rows  . Number of the rows depends on selected thumbnail size and size of the control window. Thumbnail size in a single row display depends on size of the window while the maximal size of thumbnails is given by the selected
. Number of the rows depends on selected thumbnail size and size of the control window. Thumbnail size in a single row display depends on size of the window while the maximal size of thumbnails is given by the selected  size button.
size button.
When you right click the image preview, a context menu appears with the following options:
Contextual Menu Items
Use the three top commands to create a reference image, to load the reference image and to switch between the current and reference image.
When you place the cursor over the image preview, a tooltip containing information about name, filename, path, dimensions, size, and calibration is displayed.
A scale can be displayed in the preview image. Its length is estimated automatically in order to be readable and depends on the image size. The units used depend on the image calibration.
Choose the rescaling method: linear or quick.
Displays the reference image in the window.
This command closes the opened image.
This command displays a dialog-window where all meta-information of the current image is shown. The dialog differs according to type of the image. All records are editable, some of them have predefined possible values. For more information see File > Image Properties.

Opens the Organizer pad for image files and database work. Please see Organizer for more information.

(requires: Advanced 2D Tracking)
This command opens the Polar Graph panel. For more information see: Visualization.

The preview control image shows a thumbnail of the whole image. The red rectangle indicates position of the currently observed area when the image is zoomed in. The size and position of this rectangle can be changed by mouse - the view of the image changes accordingly.
This control window displays a graph and values of the color spectrum (x-axis). The y-axis displays the mean value of the channel inside the whole image, ROIs or the value defined in the stored spectra.
The following buttons are available:
Performs spectral unmixing. A new unmixed document is created. See Image > Spectral Unmixing Setting for more details.
Opens the Image > Manage Stored Spectra command.
Curves of all ROIs are displayed in the graph regardless of the selection in the ROI list.
 Export
Export Exports the selected results into various output formats.
 Vertical Scale Absolute
Vertical Scale Absolute Displays absolute values on the y-axis.
 Vertical Scale Normalized
Vertical Scale Normalized Displays normalized values on the y-axis.
 Scale to Cursor
Scale to Cursor Displays values which are re-calculated using the value under cursor on the y-axis. The re-calculation assumes that the value under cursor is displayed as 1 and other values are re-calculated with this ratio.
 Free Cursor
Free Cursor Displays movable line cursor.
 Cursor to Maximum
Cursor to Maximum Moves the cursor to the maximal value.
 Cursor to Minimum
Cursor to Minimum Moves the cursor to the minimal value.
 Options
Options Opens the Spectrum Profile Options dialog enabling to customize the graph area.
 Find Spectra
Find Spectra Performs searching for spectra using Blind unmixing. Found spectra are displayed in the Spectra list.
 Range
Range Inserts two vertical auxiliary lines into the graph area. These lines can be freely moved to set a wavelength range. Lower range value, higher range value, middle value and the range value between the two lines is displayed next to the icon of this function.
 Store Spectrum
Store Spectrum Opens the Store Spectrum dialog window allowing to store selected ROIs as a user defined spectrum.
Data Tab
The Data Tab displays the following values in columns: Wavelength and one column for each selected ROI and Spectra.
Spectrum Profile Options
You can set all your preferences in this window. Define the minimum and maximum wavelength value, background color of the graph, and visibility of each axis during scrolling. The option AntiAlias smooths the edges of the graph line. Also you can set all the cursor and scale pen properties.
Note
When defining the Minimum/Maximum wavelength values manually, the difference should be at least 80 nm. Otherwise the system will stretch the values automatically.

Synchronizer compares (runs and views) two or more ND2 files at the same time.
See Synchronizer for more information.

This control window indicates the system state. You can display information about the session time, experiment time elapsed, X, Y, and Z position.
The arrows indicates the motion. The Last move statement indicates that Z device has stopped moving. The arrow orientation indicates the direction of the motion. The Moving statement indicates that the Z device is moving up or down (again the arrow indicates the direction).
 Settings
Settings Opens the Settings dialog which can be used to select basic system information which is displayed in the list of the System Information window.
Check this item to reverse the indication of Z moving.
Selects/deselects all items in the list.
 Show/Hide Graph
Show/Hide Graph Displays/hides the graph view.
 Select Graph Variables
Select Graph Variables Opens a dialog enabling to select which variables are shown inside the graph.
 Run
Run Starts to monitor selected variables and displays them in the Graph.
 Pause
Pause Pauses the variable monitoring.
 Reset
Reset Resets the graph view.
 Export
Export Once the graph area is paused this function exports data/graph into MS Excel, clipboard or into a file.
If turned on, only changes of the variable are shown inside the graph (time is ignored).

Displays the Volume Options dialog window. Please see Volume Options.

Displays the Z-LUTs for Volume View.
Z-LUTs graphically depict the intensity values through the whole Z dimension of a volume image. Turn Z-LUTs on by clicking  Turn Z-LUTs On or Off. Range profile (main graph showing the intensity values) can be stretched using the slider below making it possible to display low intensity values of the graph. Zooming tools are available in the bottom right corner.
Turn Z-LUTs On or Off. Range profile (main graph showing the intensity values) can be stretched using the slider below making it possible to display low intensity values of the graph. Zooming tools are available in the bottom right corner.
Circular anchor points of the left and right graph axes can be used to precisely adjust the noise vs. signal ration in any Z-position of the 3D image. Double-click on the left vertical axis to add an anchor point into the graph or grab a predefined one (white circle) and move it to the right to remove noise in the particular area of the volume image. Moving the anchor points on the right vertical axis to the left increases the signal strength. Double-click on a circle to delete it or use the  Reset to default state button to reset the graph into default. To remove a portion of the data define a Low and High Quantile (percentage of intensities on the sides of the intensity spectra) in Z-LUTs Options.
Reset to default state button to reset the graph into default. To remove a portion of the data define a Low and High Quantile (percentage of intensities on the sides of the intensity spectra) in Z-LUTs Options.
 Turn Z-LUTs On or Off
Turn Z-LUTs On or Off Adjustments made in the Z-LUTs for Volume View panel are shown/not shown in the Volume Viewer.
 Reset to default state
Reset to default state Resets the Z-LUTs for Volume View panel into default.
 Orientate Volume to Match Graphs
Orientate Volume to Match Graphs Rotates the volume view so that it matches direction set in the Z-LUTs for Volume View panel.
Selects the channel onto which the Z-LUTs adjustments are made. To see all channels at once select the All option.
 Z-LUTs Options
Z-LUTs Options Turns on/off the Mean Z-Curve and Range Profile. It is also possible to enter where Low and High Quantile values can be set and Mean Curve, Min/Max Range Profile and graph Z-order flipping is enabled.
 Modify Data through Z-LUTs
Modify Data through Z-LUTs Applies Z-LUTs settings to the image data - the original image will be overwritten. Until you press this button, no changes are made to the image data.
 Save/Load Z-LUTs settings
Save/Load Z-LUTs settings Saves/loads the current settings of the Z-LUTs for Volume View panel into/from a .zlu file.

This control window displays a list of all recently executed commands and manages them. You can also use this control window to easily create a macro from a sequence of recently used commands.
See Macro > Command History for more information.

The Debug View can be used to control the current macro execution. It displays the source code of the macro. When the macro runs, the executed line is indicated by an arrow. If there are any breakpoints put into the source code, the macro execution stops there.
The following buttons can be used to debug the macro:
 Go
Go Executes the macro from the current position to the end or to the nearest breakpoint.
 Next Step
Next Step Executes the macro by the smallest steps. Each time the button is pressed, the execution moves one step forward.
 Interrupt Macro Execution
Interrupt Macro Execution Pauses macro execution.
 Add/Remove Breakpoint
Add/Remove Breakpoint When a line is selected, a breakpoint is added/removed by pressing this button.
 Clear Breakpoints
Clear Breakpoints Removes all breakpoints from the current macro.
 View Variables
View Variables Opens the Variables control window.
 Edit macro
Edit macro Opens the currently executed macro in a separate window. User can modify the macro.
See Also
View > Macro Controls > Variables 

This control window displays chosen macros and/or commands as buttons. Macros and commands can be run by clicking on their button representative, or using a hotkey defined in the Setup Macro Panel.
Control Window Options
 Regular Buttons
Regular Buttons Use this command to change size of the buttons to be the same width. When this button is not pressed, buttons wrap the title (a text or an icon) of the button.
 Add Command
Add Command This command opens the Paste Command dialog. You can choose a command, which is added to the Macro Panel.
 Add Macro
Add Macro This command opens the Add Macro dialog. You can select a predefined, shared or recently used macro or a macro from a file, which is added to the Macro Panel.
 Setup Macro Panel
Setup Macro Panel Opens the Setup Macro Panel window. You can manage the macros and commands and their properties.
 Associate with Current Layout
Associate with Current Layout When this button is pushed, different contents of the control panel are saved for each layout.
How to add a command
How to add a macro
The buttons can be rearranged in the panel by drag and drop. Title of the button can be renamed using the Rename command from the context menu.
Setup Macro Panel Options
Overview of added macros and commands is displayed in this window. Name of the command or full path to the macro is visible in the first column. The second column shows names of the commands/macros. The third column displays assigned hot keys. The forth column contains preview of the button in the Macro Panel. You can directly edit the name, hot key or preview, if you left-click the corresponding field of the selected command/macro.
 Add Command
Add Command Opens the Paste Command dialog.
 Add Macro
Add Macro Opens the Add Macro dialog.
 Edit
Edit Opens the Macro Editor window.
 Properties
Properties Opens the Properties dialog.
Moves the selected macro or command one line up/down.
 Remove
Remove Removes selected command or macro.
 Remove All
Remove All Removes all commands and macros.
Loads the saved definition from an external XML file.
Saves the definition to an external XML file.

The Variables control window displays values of variables present in the currently running macro. A control window with four tabs appears:
This tab displays all user defined variables of the currently running macro and their values. If no macro has been run, the table is empty.
There are some variables predefined within NIS-Elements. Their current values are displayed in this table.
System constants are listed within this tab.
A selection of local and global variables can be displayed within this tab. Write a variable name to the Name field, or if you right click the variable name within the Locals/Globals tabs, a context menu appears with the Send to watch option to be selected.
This command toggles Look Up Tables. This command is equivalent to pressing the LUTs button, placed on the NIS-Elements main toolbar in the upper left corner. When LUTs are activated, this button turns red.
Note
To see how to set and use look-up tables, see LUTs - Non-destructive Image Enhancement.
This command runs the auto scale procedure permanently (on the live image). This command corresponds to the  button in the top document toolbar.
button in the top document toolbar.
This command adjusts the white slider position of all channels automatically with the purpose to enhance the image reasonably. This command corresponds to the  button in the top document toolbar.
button in the top document toolbar.

This command shows the LUTs control docking window. Look-up tables are used for image color and brightness modifications.
See detailed description of LUTs functionality and control in the LUTs - Non-destructive Image Enhancement chapter.
This command defines a custom LUTs gradient. The left side of the window contains a list of all already defined gradients. Use buttons from the middle portion of the window to manage them. Start with creating a new gradient by clicking the button, name it and define its appearance in the right portion of the window which provides the gradient's overview. You can change the name of the gradient directly in the Name field. Then enter which pixel Intensity value is assigned to a selected color. After you fill in one row, another one is created automatically. When done with defining your gradient, you can press the button and choose the gradient from the LUTs window pull-down menu or it to your image immediately.
Creates a new LUTs gradient. Enter the name of your gradient.
Removes the selected LUTs gradient.
Duplicates the selected LUTs gradient. New name needs to be filled in.
Saves the gradient to an external XML file.
Loads a previously saved gradient.

 Up / Down arrows
Up / Down arrows Clicking the arrow button moves the selected gradient one line up / down in the list.
Edit the name of your gradient in this field.
Check this item to make smooth color transitions between defined colors.
When checked, the gradient uses only discrete pixel intensity values with no color transitions between defined colors.
Defined colors are stretched symmetrically across the whole intensity range with 50% in the middle.
Define the range of pixel intensity (in percentage), which corresponds to the appropriate Color.
Use this color picker for selecting the pixel intensity value directly from the image.
Shows the chosen color. Press the ... button to choose an arbitrary color.
Use this button to reset the currently selected colors to a default gradient.
Displays the relevant help page.

Displays ND document in the main view. See ND Views for more information.

This command displays the sequence of images as a 3D model using perspective projection. Please see Volume Viewer.

This view displays frames of the selected dimension arranged one next to other. (Requires Z, T or XY dimension).
One or two dimensions can be viewed at a time.
Window Options
Drag the slider to change size of the tiles.
 Fit to screen,
Fit to screen,  1:1 Zoom,
1:1 Zoom,  Zoom In,
Zoom In,  Zoom Out, N %
Zoom Out, N % You can use these zoom buttons as in the standard image window. The resulting zoom is relative to a single tile.
See also Image Window
Select the dimension to be displayed within this pull-down menu.
Performs maximum intensity projection on the selected dimension (Time or Z-stack) of the ND document.

Press this button to display the Layout Settings window:
Layout Settings
You can change the way the tiles are displayed. Press the Layout Settings  button in the top image toolbar. The following window appears:
button in the top image toolbar. The following window appears:
Layout Options
Calculates the number of columns automatically.
Define the number of columns by entering a value.
Frames of a multi-point ND2 file can be displayed in the layout matching the XY stage positions which were used during the acquisition.
Define whether the thumbnails are displayed in rows or a meander. Also define in which corner shall the first frame be placed.
Numbering
Numbers may appear on the tiles if you wish. Set the options here:
Select whether and how the numbers / letters are displayed in tiles. Possible options are None, Numbers, Uppercase letters and Lowercase letters.
Specify the text area position within the tile.
Define text color and select a font.
Define background color of the text area inside.
Other Options
Check this item to highlight the currently selected frame by a red frame.
Check this item to display the information under each frame.
Check this item to keep the tiles apart by a distance. Define the space size between the tiles in pixels.
Check this option to use the default background color for the tiled view. Otherwise, you can pick any color from the Background color palette.
A header/footer can be displayed within the tiled view. Select the check-box to enable this feature. When you place the cursor over the header/footer area, a button appears, press it to switch to edit-mode.
Check if you want to display the user events.
Select the header and footer background color.

This command displays a new window for exploring the slices of an ND2 file.

Displays ND document in the maximum intensity projection. See ND Views for more information.

Displays ND document in the minimum intensity projection. See ND Views for more information.
This command turns on a special view where each component of the image is displayed separately while zoom and view position are synchronized.
This command shows or hides probe. It is equivalent to the  button placed as most upper on the right side of image window. To change the probe appearance, invoke the View > Layers Properties > Probe Properties command.
button placed as most upper on the right side of image window. To change the probe appearance, invoke the View > Layers Properties > Probe Properties command.
This command shows or hides the background probe. It is equivalent to the button placed on the right toolbar of the image window.
Displays graticules plane in a defined appearance. It is equivalent to the  button placed in the right toolbar of the image window. To change the graticules plane appearance, invoke the View > Layers Properties > Graticules Properties command.
button placed in the right toolbar of the image window. To change the graticules plane appearance, invoke the View > Layers Properties > Graticules Properties command.
Displays/hides the scale. It is equivalent to the  button placed in the right toolbar of the image window. To change the scale appearance, invoke the View > Layers Properties > Scale Properties command.
button placed in the right toolbar of the image window. To change the scale appearance, invoke the View > Layers Properties > Scale Properties command.
Context menu over a scale
Inserts the current scale layer into the image so that the scale becomes part of the image.
Moves the scale bar into its default position.
Locks/unlocks the scale bar in its position.
Displays/hides the measurement frame. When ON, binary objects outside the frame are omitted when performing automatic measurement. Actual settings of the frame behaviour can be set by the Measure > Options command. The frame size and position can be adjusted by mouse, or specified precisely within the Measure > Measurement Frame command window.
This command displays the LUTs color scale inside the current image. Positions of the Black, White, and Gamma sliders is indicated on the scale.
Note
The scale is available for monochromatic (gray-scale) images only.
This command displays/hides the annotation layer. It is equivalent to the  button placed in the right toolbar of the image window.
button placed in the right toolbar of the image window.
See Image Layers for further information.
Displays the area of measurement (measurement region of interest). See also Introduction to ROIs.
Displays the current binary image.
Note
The command corresponds to the binary button on the right side of the main NIS-Elements window. CTRL+B is the shortcut key.
Displays the current color image.
Note
It corresponds to the color button on the right side of the main NIS-Elements window. CTRL+R works as a shortcut key.
Displays both the current color and the binary image.
Note
It corresponds to the overlay button on the right side of the main NIS-Elements window. CTRL+V is the shortcut key.
This command changes the color of binary image displayed in the overlay mode. The overlay can be displayed in sixteen different basic windows colors.
This command decreases transparency of binary image displayed in overlay.
This command increases transparency of binary image displayed in overlay.
This command displays window for setting up the probe properties. You can reach this command by left-clicking on the Show probe button (located on the toolbar in image window) too.
Sets color of the boundary line.
Sets thickness of the boundary line.
Sets the position of x-coordinate of the top left corner of the probe rectangle.
Sets the position of y-coordinate of the top left corner of the probe rectangle.
Sets width of the probe.
Sets height of the probe.
If checked, the probe remains always visible while zooming and scrolling the image.
This command displays window for setting up the graticule properties. You can reach this command via context menu on the Show graticule button (located on the image toolbar).
Sets the type of displayed graticules:
Most grid types consist of primary and secondary lines. Their color can be selected from these pull-down menus.
The thickness of graticule lines can be selected.
The density value - the closest distance between two line intersections of a graticule - can be set in the edit box, or you can let NIS-Elements adjust it automatically according to the current zoom factor. The units selection depends on the image calibration (calibrated/uncalibrated).
Adds vertical lines to the grid.
This command displays a window with the scale properties.
Scale Tab Options
Sets the horizontal or vertical orientation of the scale.
Sets the shape of the scale.
Sets the size of the scale. If the Automatically adjust size option is ON, the Size edit box becomes disabled and the system computes the optimal size according to the image calibration and zoom factor.
Sets the scale bar color.
Sets the thickness of the scale bar line.
Sets the scale background color. This is handy if your image has lots of colors and it is difficult to choose a contrasting color for the scale.
This option dynamically places the scale so that it is always visible, even if you zoom in or shift the image.
This option hides/displays the scale legend.
Check this item to enable the automatic scale size adjustment based on the image calibration and zoom factor.
Size relative to the image width can be selected here. To enable this function check the above option first.
This option determines how the inserted scale will be resized - it can prevent inserting a too small or too large scale. Original burns the scale in the size as you see it in the image in the current zoom. Fit to Screen burns the scale as if you zoomed the image to the Fit to Screen mode and applied the Original method. 1:1 burns the scale as if you zoomed the image to 100% and applied the Original method.
Font Tab Options
Standard font properties of the scale legend can be adjusted within the Font tab:
This command displays the measurement frame and a window for setting up the measurement frame properties. It can be also displayed from the context menu on the Turn Frame on/off button on the right image toolbar.
Sets the frame line color.
Sets the frame line thickness.
Sets the frame left corner coordinates.
Sets the frame dimensions.
You can select the units of the measurement frame. Pixels and the calibration units are available in case of a calibrated image.
This command displays a window for setting up the intensity profile properties. The appearance and behaviour of the graph can be modified in the Intensity Profile Options window. Press this  button to display it from the control window. For more information see Measure > Intensity Profile
button to display it from the control window. For more information see Measure > Intensity Profile  .
.
The window contains three tabs:
General Options tab
Choose background, axes and grid colors from the palette. Then check the Show ... Grid items if you want to make them visible in the graph. Check the relevant .. Axis Always Visible item to make the axis always visible while zooming in the graph.
Select interpolation method for data treatment by pressing the relevant button. You can choose Steps, Linear, or Bicubic interpolation method.
Check to use logarithmic scale in the graph.
Check this item to display data points. Small dots indicating the actual data values position can be displayed on the graph line. The points appear only if the distance between them is big enough for them to be recognized (so they usually appear when you zoom in the graph).
Turning this option on will make the graph line edges look smooth.
Check this item to fill in the area under the line chart with a color. Select the amount of opacity used from the list of predefined values.
Check this item to display or hide X, Y coordinates of pixels in the Data tab of the Intensity Profile control window.
If two profile lines are used, this feature highlights the second line inside the graph view.
Set the profile line appearance. You can change its color, width and style, line thickness.
Note
These settings are applied to the profile line displayed over the image as well as to the graph lines, with only one exception: If image channels have their color specified (e.g. RGB image), the graph lines are displayed in this color and the color specified within this window is ignored.
By defining a neighborhood, you extend the source area from 1pixel line to a stripe. Specify the Width of the stripe and its units - in (pixels, microns) and select which value to display within the graph:
Check Display in the image to visually indicate the neighborhood in the image.
Note
If a custom value, which is not listed in the Width box, is entered, the neighborhood measurement may be performed in an area narrower than specified due to pixel truncation.
Define colors of lines and labels used in the graph when objects are measured.
When you click into the graph area, a vertical line appears in the graph and the “Indicator” appears in the image as well. Indicator is a line which displays the position on the profile line corresponding to the mouse position in the graph. You can select its color within this pull down menu.
Select pixels or the current calibration units for the Shift Left/Shift Right buttons in the tool bar.
X axis
The Auto option enables that the range values are set automatically. On the contrary the range values can be set on Fixed values also. The range values can be set for minimum of X axis, maximum of X axis, major and minor grid of X axis.
If you select the Best Fit option, zoom of the X axis will be set to best fit. Otherwise you can set the Fixed range.
Y axis left
The Graph Range and Zoom options are described above.
Set the line appearance - line color (in case color of image component is not set), thickness and style (solid, dot, dashed, dash-dot).
Set the second profile line appearance - thickness and style of the line (solid, dot, dashed,dash-dot). Check the Color highlighting to highlight the second profile line in the graph.

Hides all screen elements such as menus, buttons, status bar etc. To return the hidden elements to the screen press ESC key.

Adjusts the zoom factor to view exactly the whole image as big as possible.

Fills the screen with an image and crops the view of its marginal parts in one direction. The scroll bar appears on one side of the screen only.
Displays the window for setting options for Magnifier Glass tool. The Magnifier Glass can be activated by the button in the upper left corner of NIS-Elements screen.
Magnification of Magnifier Glass.
Size of the Magnifier Glass.
Magnifier Glass can be either circular or square.
Color and thickness of border.
The image displayed in Magnifier Glass can be enhanced by gamma correction in order to see the details brighter. The value for gamma correction is set in the box below.
If checked, magnified image is shown next to the cursor whereas if unchecked, the magnified area is displayed around the center of the cursor.
This command selects the displaying mode of LUTs in spectral images. See LUTs on Spectral Images for more information about each mode.
This command displays all color channels of the current image in the overlay mode and can be used to select a single component to display.
In this menu it is possible to set the component to be shown and processed. Selected component is marked by the check mark on the right side. This command works the same way as switching the proper channel tabs manually in the image window.
Opens the Streaming Tool dialog window used for setting the streaming parameters. The stream is turned on by the View > Start Streaming function. Multiple users can access the streamed video signal and watch the screen of the streaming device. The stream can be password protected so that it is viewed only by clients knowing the password. To be able to use this function, Screen sharing option has to be selected during NIS-Elements installation.
Dialog Window Options
Internet - is used for streaming through an Internet service. In the Server drop-down menu, select a predefined Internet streaming service. Then click on the link below redirecting you to the website of the selected service. There you should register and acquire a streaming key. Enter this key into the Stream Key field. The  button can be used to show the hidden characters.
button can be used to show the hidden characters.
Server - is used when the streaming server is installed on a different computer available on a network for NIS-Elements as well as for all clients. Enter the IP address into the Server edit box, check whether to access the stream with a password (Use Password) and click to register this copy of NIS-Elements for streaming on this server. To register this device on a different server, click . Click on the generated link to see the stream or use and send the address to all clients which are about to watch the stream. To be able to use this option, Streaming Server has to be installed (contact your distributor to acquire the installation file).
If turned on, cursor is included in the streaming video.
Starts streaming.
Closes the Stream Tool dialog window.