Reduces N source frames into one resulting frame. Each pixel value in the resulting frame is an average of corresponding pixels in N source frames.
Based on the type:
All frames in the loop are reduced into one frame (all to 1).
For each frame in the loop reduces surrounding N frames into the current one (all to all).
Reduces every consecutive N frames into one frame (all to all/N).
Loop to be reduced.
Number of frames to reduce. Disabled for All Frames.
Finds the best focus plane in the whole loop and effectively reduces the loop into single frame.
Select the method matching the acquisition modality.
Loop to be reduced.
In case there are more channels (All) select the one to use for criterion calculation.
(requires: EDF Module)
Creates an Extended Depth of Focus (EDF) image from the selected Z-Stack Loop similarly to the Applications > EDF > Create Focused Image  For more information about EDF please see Extended Depth of Focus.
For more information about EDF please see Extended Depth of Focus.
Integration uses multiple source frames to create one resulting image by integrating their pixel intensities. This is useful especially for low-signal (dark) scenes.
All frames in the loop are reduced into one frame (all to 1).
For each frame in the loop reduces surrounding N frames into the current one (all to all).
Reduces every consecutive N frames into one frame (all to all/N).
Loop to be reduced.
Number of frames to reduce. Disabled for All Frames.
Displays ND document in the maximum intensity projection. See ND Views for more information.
Reduces the specified loop by taking a pixel from Channel stack A from the frame where the Reference channel stack Ref has maximum intensity.
Performs median on the connected result based on the specified parameters.
All frames in the loop are reduced into one frame (all to 1).
For each frame in the loop reduces surrounding N frames into the current one (all to all).
Reduces every consecutive N frames into one frame (all to all/N).
Loop to be reduced.
Number of frames to reduce. Disabled for All Frames.
Performs quantile on the connected result based on the specified parameters.
Displays ND document in the minimum intensity projection. See ND Views for more information.
This action is used for selecting a specific frame in the source image.
Loop where the frame will be selected.
Specifies the selection from the current loop.
Starting frame.
Number of frames.
Step size.
Selects one frame (Index) from the specified dimension (Loop).
Returns binary from a selected frame (Index) chosen from the specified dimension (Loop).
Captures a shading image of the selected Type on the selected Loop. See also Image > Background > Shading Correction.
(requires: Stage)
Stitches frames of the connected image into a large image. Select the stitching method from the Stitching via drop-down menu (see Methods Used for Stitching Large Images). Optionally the Precise stitching (Image Registration) can be checked but be aware that it is more computationally demanding.
Optionally use the Automatic Shading Correction and choose the type which best represents your sample - Brightfield, DIC like or Fluorescence with offset enabling to heighten brightness level of the corrected image to make objects in dark areas more visible.
Reduces N source frames into one resulting frame. Each binary pixel in the resulting frame means that every frame has this binary pixel. The function behaves like Min IP but on the binary.
All frames in the loop are reduced into one frame (all to 1).
For each frame in the loop reduces surrounding N frames into the current one (all to all).
Reduces every consecutive N frames into one frame (all to all/N).
Loop to be reduced.
Number of frames to reduce. Feature is disabled for All Frames.
Reduces N source frames into one resulting frame. Each binary pixel in the resulting frame means that at least one frame has this binary pixel. The function behaves like Min IP but on the binary.
All frames in the loop are reduced into one frame (all to 1).
For each frame in the loop reduces surrounding N frames into the current one (all to all).
Reduces every consecutive N frames into one frame (all to all/N).
Loop to be reduced.
Number of frames to reduce. Feature is disabled for All Frames.
Moves the frames with respect to each other in order to stabilize the motion of the image.
Previous / First frame.
Loop to stabilize.
In case there are more channels (All) select the one to use for calculation.
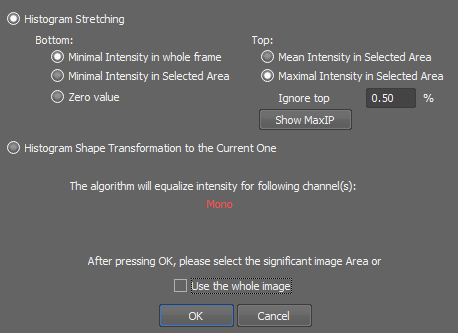
This command enhances the dynamic range of generally any current ND2 file which contains at least Z dimension. It analyses the image, calculates values similar to auto-contrast values common for the whole time sequence and then processes all frames of the ND2 file. This method is robust to noise and preserves original trends of histogram.
You can select a method used to equalize the intensity.
Select which method is used to equalize the document. The histogram is stretched using selected methods. The shape of the histogram is preserved.
This method transforms the shape of the histogram of the whole document according to shape of the histogram of the selected area.
After you press the OK button, you will be prompted to select according to which area the image will be equalized. Draw the rectangle and confirm with a right-mouse click. The document is processed afterwards.
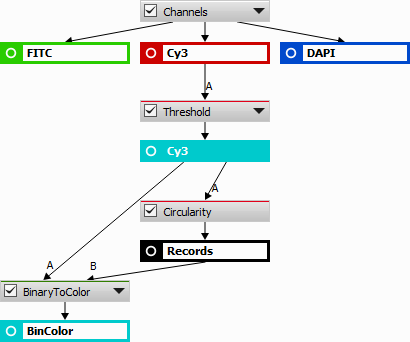
Connected binary image is converted into a color image. Pixels of the binary objects are equal to one and background pixels become zeros.
Creates a new channel with a binary filled with the measured object feature (Object value).
Example 10.
Detect objects on a channel (with threshold) and measure circularity (or any other object feature). Then use this action on the thresholded result and connect the tabular input with the circularity result. Set Object value to Circularity. Each binary object now gets a circularity value.
Value added to the background (everything except the binary).
Object feature which is written to the object linked through Entity and ObjectId.
Creates a new channel with a binary filled with the measured object feature (Object value).
Value added to the background (everything except the binary).
Object feature which is written to the object linked through Entity and Object3DId.
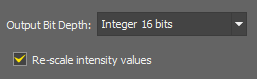
Changes the bit-depth of the connected result.
Sets a new color depth of your image. 8-bit/16-bit integer or a floating-point. Intensity values can be rescaled.
If checked the pixel values are mapped to the new range. E.g. when you convert an 8bit image to 16bit and you do not rescale the values, it results in a completely black image. If the check box was selected, the 8bit 255 value would become 65535 in 16bit etc.
See ND Processing & Conversions > Bitdepth > Change Bit Depth.
Changes the bit-depth of the connected result to the bit-depth of the connected reference image. Intensity values can be rescaled.
Splits the connected results back to the state before the channel merge.
Creates an intensity channel from the connected color source.
Converts multiple binary inputs into a color class image where every pixel belongs to exactly one class defined by its value (zero being background). Binaries are taken one-by-one from A parameter each setting a value (A -> 1, B -> 2, ...) to pixels under the corresponding binary. If binaries overlap the later is preserved.
Converts class image into multiple binaries based on the pixel values.
Number of binaries created.
Connected color image is rendered into a single RGB image.
Connected binary image is rendered into a single RGB image.
Overlay of the connected color (bottom) and binary layer (top) is rendered into a single RGB image.
Renders Channel A and Binaries B1, ..., Bn and stores it in the table as a row. If Filter is connected to a table it renders only frames present in the table.
Defines the size (in microns if calibrated) of the center portion of the frame that is cropped and rendered.
Maximum Size (in pixels) is a limit to which the rendered image is stretched down if being bigger.
Converts the connected RGB result into an intensity channel.
Converts the connected RGB result to its HSI representation.
Converts the connected HSI result to its standard RGB representation.
Creates a Volume Contrast image from the connected color image. Set the Wavelength of the connected sample image ( reset button returns the default value) and define the Well surface and Background level values. Recommended values can be added using the button on the right.
reset button returns the default value) and define the Well surface and Background level values. Recommended values can be added using the button on the right.
 ND Processing & Conversions
ND Processing & Conversions