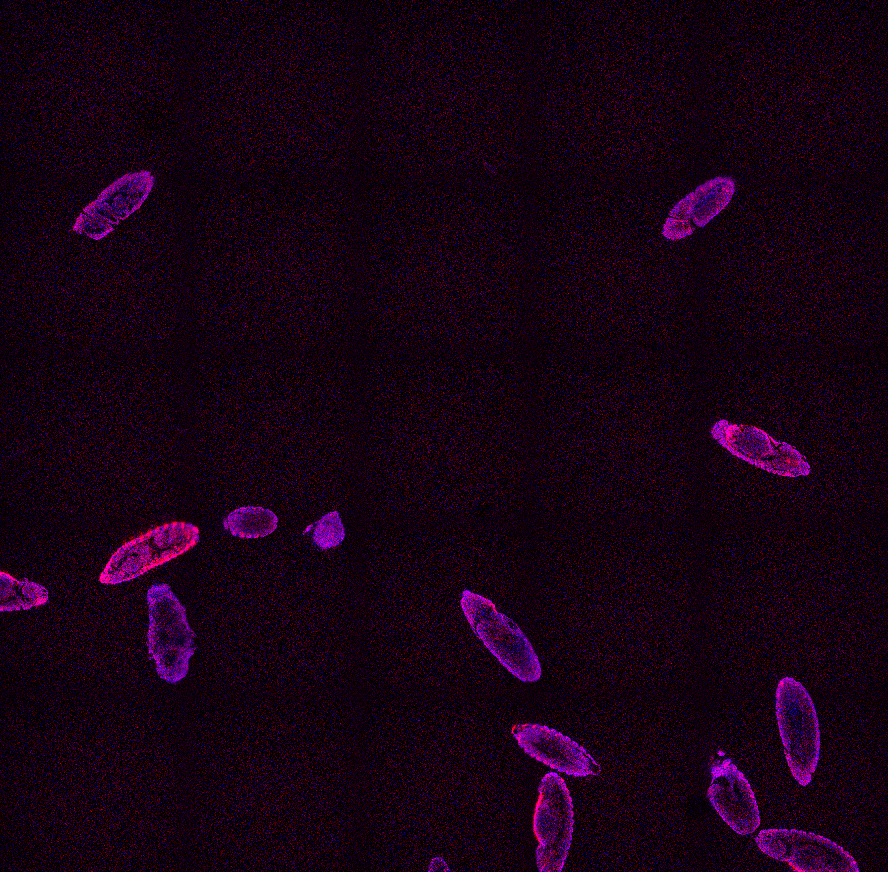
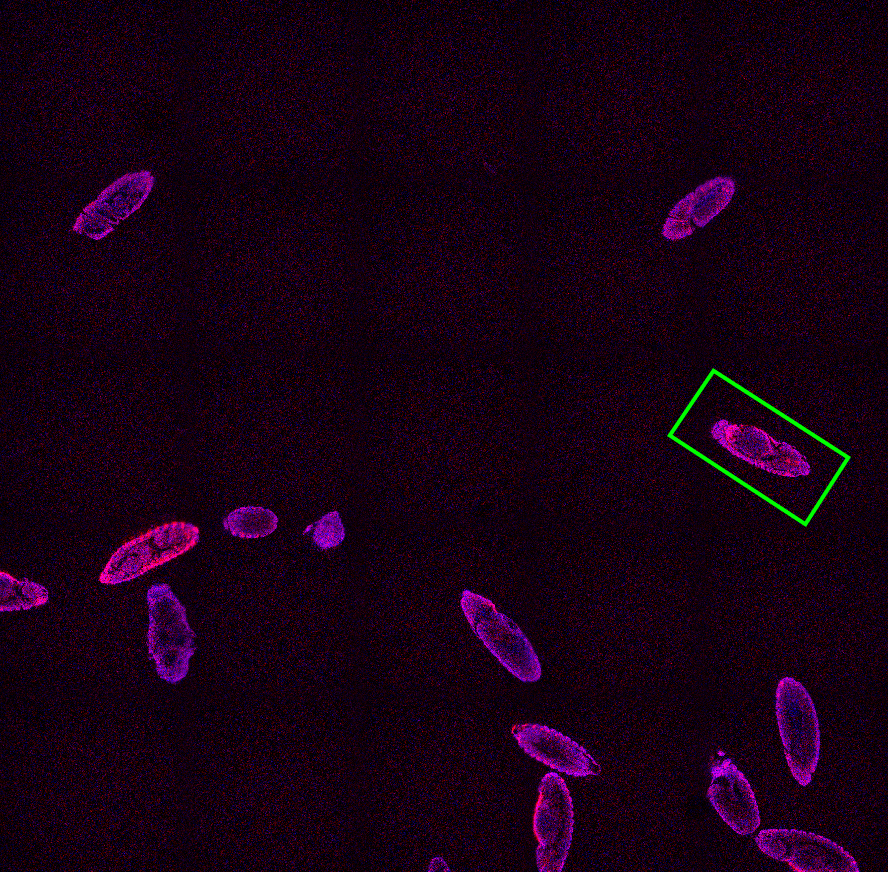
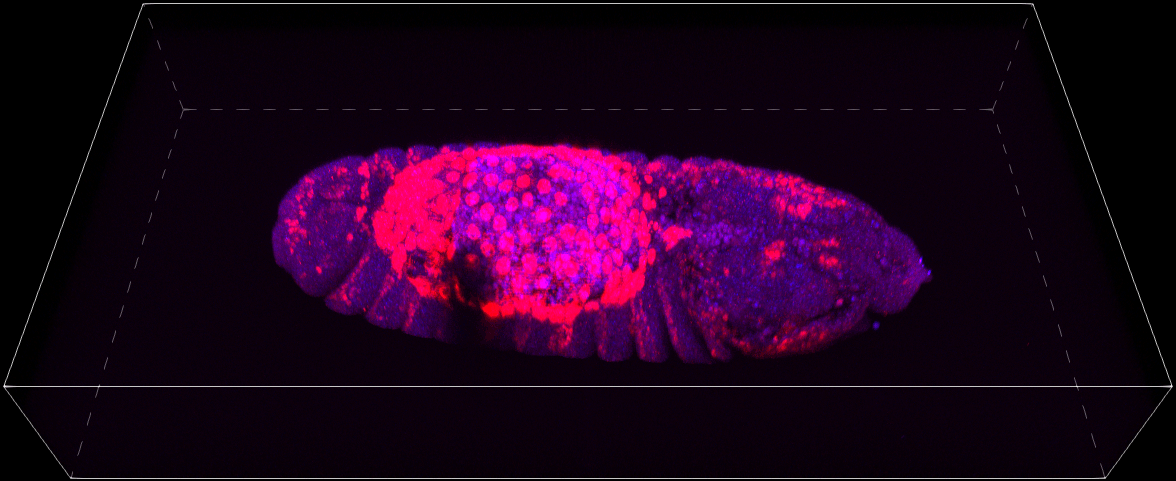
In this example Nikon A1 confocal microscope is used for image acquisition of the Drosophila melanogaster embryos. We want to capture a Z-stack of each complete embryo in high-resolution and as fast as possible.
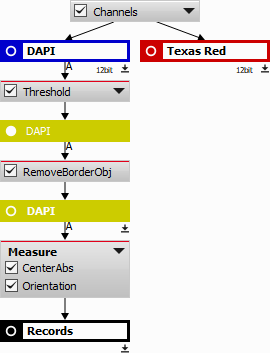
We start by defining the following General Analysis:
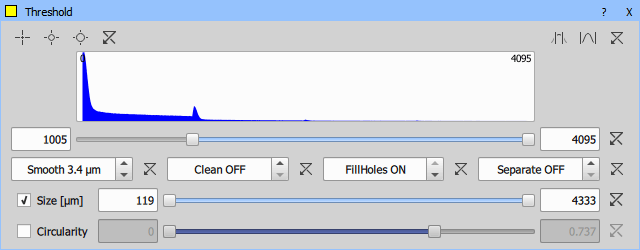
DAPI channel is used for segmenting the fruit fly embryos using Segmentation > Threshold > Threshold.
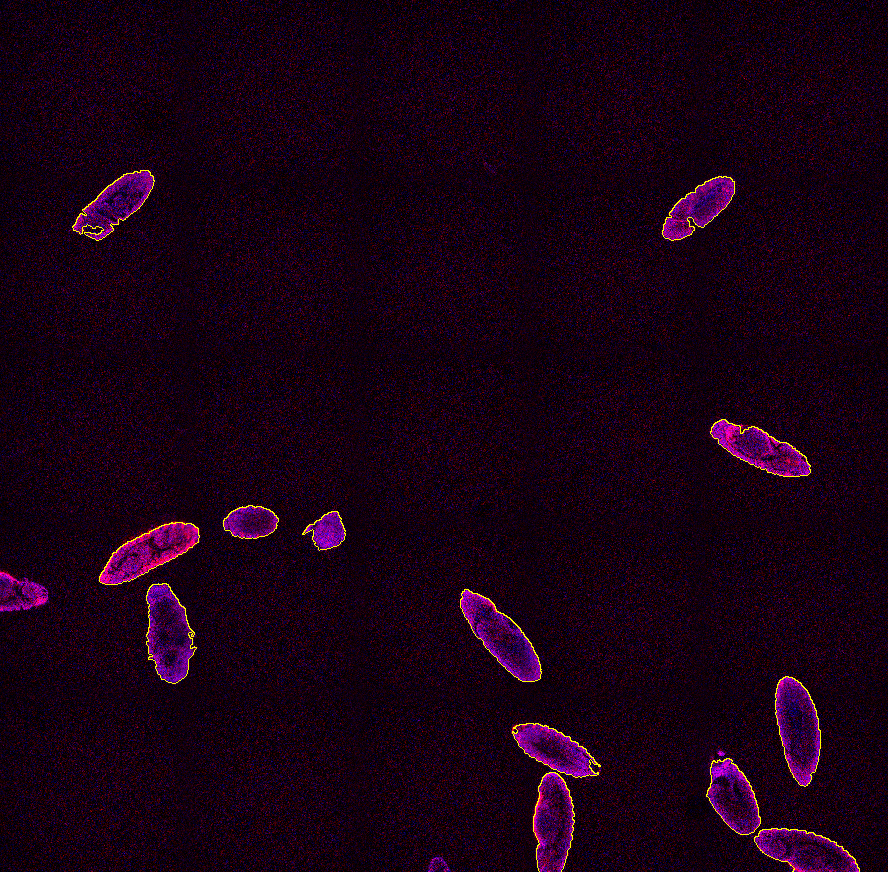
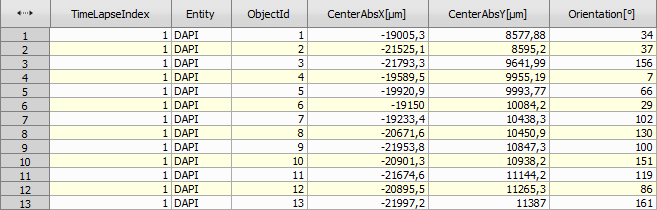
All embryos touching the image border are then removed using Binary processing > Remove objects > Touching Borders and the center of gravity for each remaining embryo (Measurement > Object position > CenterAbs) and its orientation (Measurement > Object shape > Orientation) is identified. These two variables will be necessary for the scan area positioning.
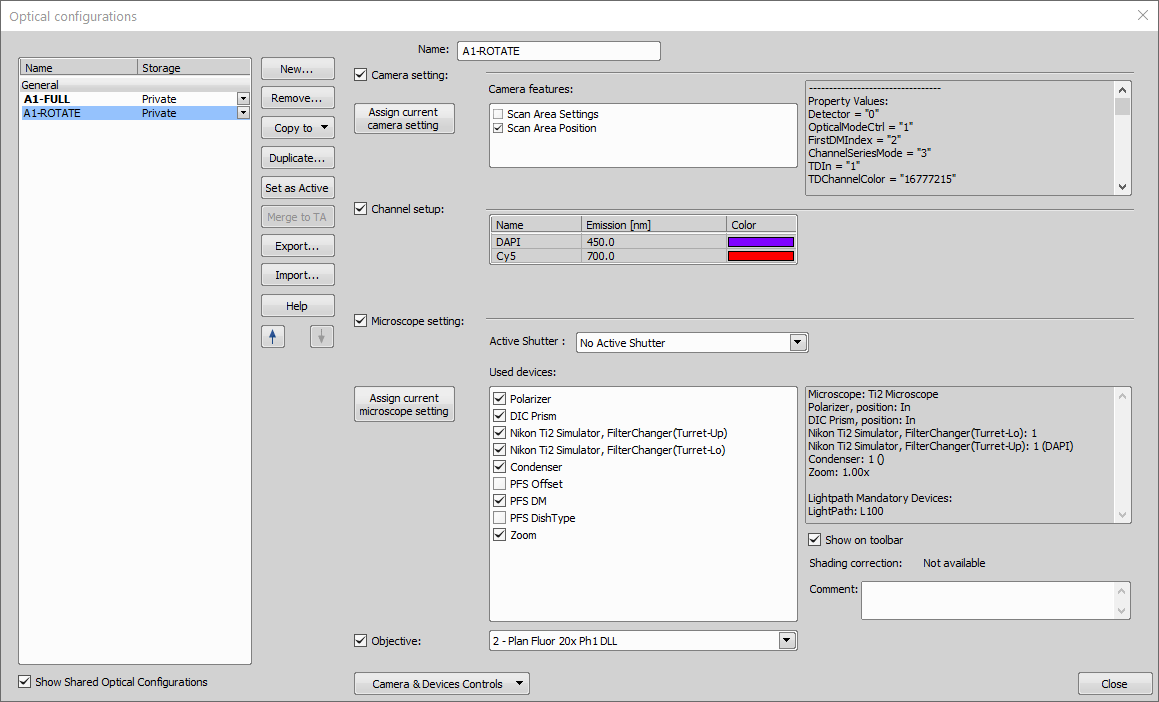
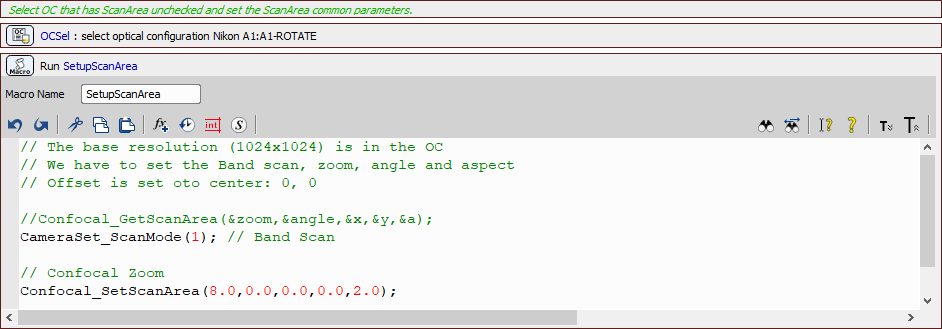
Now we define two optical configurations. One for the low magnification overview (“A1-FULL”) and one for the high magnification scan (“A1-ROTATE”) using the rotated scan area. We make sure Scan Area Settings is unchecked for the latter configuration.
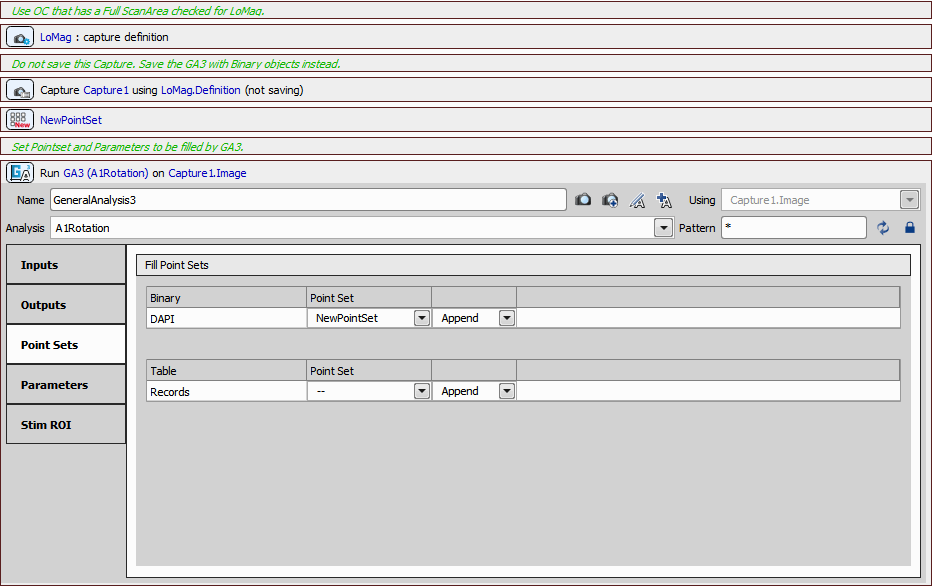
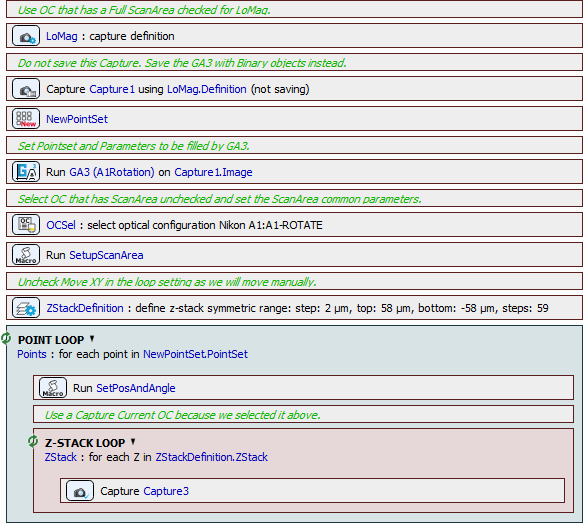
We can move on by defining a new Job. Low magnification capture is set (Acquisition >  Capture Definition) with the “A1-FULL” optical configuration. Then a new point set (Stage XY Points >
Capture Definition) with the “A1-FULL” optical configuration. Then a new point set (Stage XY Points >  New Point Set) is added and filled with the General Analysis 3 data acquired before.
New Point Set) is added and filled with the General Analysis 3 data acquired before.
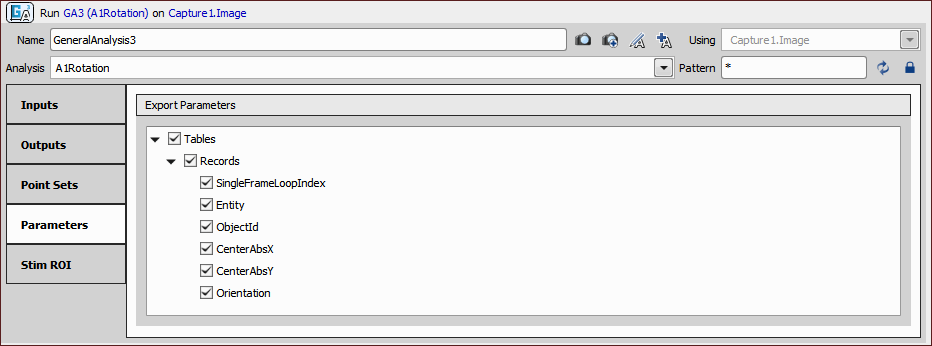
We check all the records available from the selected general analysis (Analysis >  General Analysis).
General Analysis).
Then we select the “A1-ROTATE” optical configuration (Optical Configurations >  Select Optical Configuration) and use two macro functions (System >
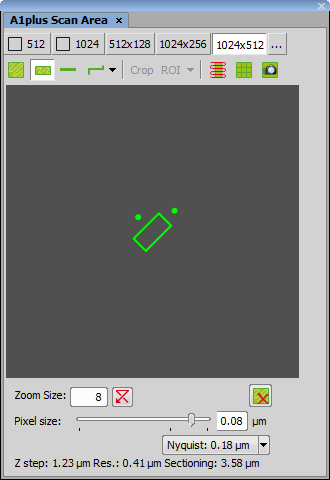
Select Optical Configuration) and use two macro functions (System >  Macro) to select the Band Scan scan mode and set the zoom size (8) and shape of the area (2 by 1 rectangle of 1024 x 512).
Macro) to select the Band Scan scan mode and set the zoom size (8) and shape of the area (2 by 1 rectangle of 1024 x 512).
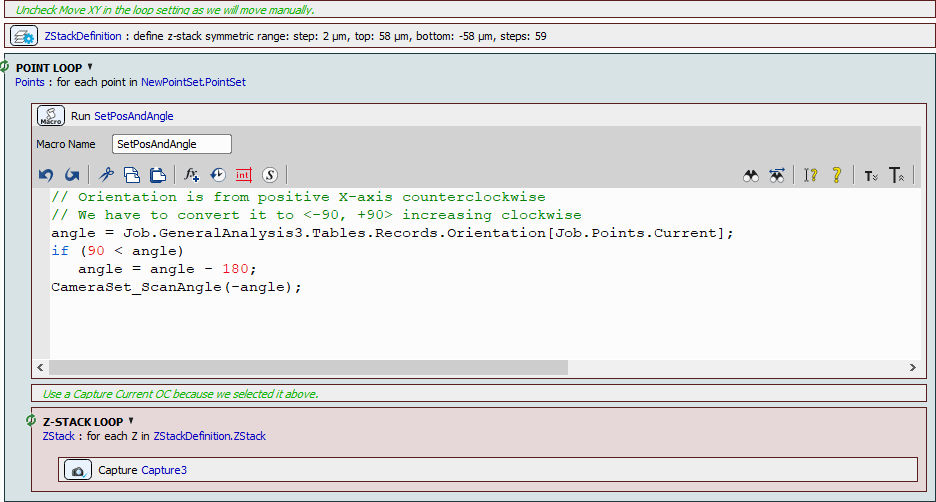
Z-Stack for the high-resolution acquisition of the embryo is defined (Z-Stack >  Define Z-Stack) and another macro setting the proper orientation of the scan area is placed inside a point loop (Stage XY Points >
Define Z-Stack) and another macro setting the proper orientation of the scan area is placed inside a point loop (Stage XY Points >  Loop over Points) together with the Z-Stack loop (Z-Stack >
Loop over Points) together with the Z-Stack loop (Z-Stack >  Z-Stack Loop) capturing the final images.
Z-Stack Loop) capturing the final images.
Now the job is complete and can be executed. Data from the General Analysis 3 are used to properly position the scan area over each embryo and capture the high-resolution Z-Stack.