Define Z-Stack
Define Z-Stack This task defines parameters required for capturing a Z-Stack (a sequence of images each having a different focal plane). Please see the Z-series Acquisition chapter for details about the Z-stack setup. Create all-in-focus images or 3D models regardless of your sample and depth of field parameters. | Requires: Device: Stage Z |
Name of your Z-Stack >  Define Z-Stack task.
Define Z-Stack task.
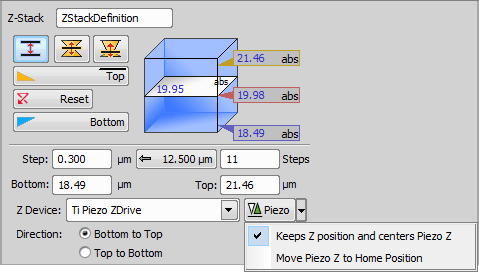
This mode defines the Z-stack using two parallel planes ( ![]() Top and
Top and ![]() Bottom).
Bottom).
Required values: top position, bottom position, step size or number of steps.
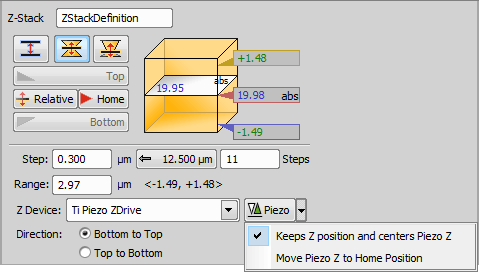
This mode defines the Z-stack by its center (Home) position and the same range above and below the Home plane.
Required value: range.
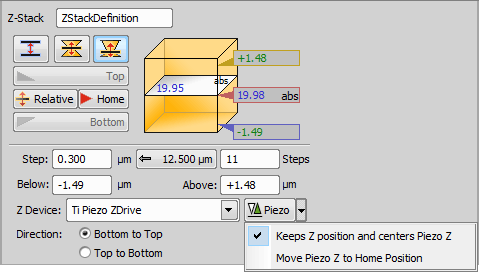
This mode defines the Z-stack by a center (Home) position and a custom range above and below the Home plane.
Required values: above position, below position.
Sets the top Z position.
 Reset
Reset Discards the Top, Home, and Bottom position settings.
Changes the Home (absolute Z) position to Relative (current Z position deducted prior to the actual acquisition).
In the Symmetric / Asymmetric mode defined by range this button sets the position in the middle of your range.
Sets the bottom Z position.
Define the range of a single step.
Click this button to use the recommended step size.
Insert the number of steps you want to acquire.
Set the bottom Z position manually.
Set the top Z position manually.
Choose a Z device used for Z-stack acquisition.
Specifies the role of the Piezo Z drive.
Enter the range of the final Z-stack (in-focus portion of your sample).
Set the bottom position of the Z-Stack manually.
Set the top position of the Z-Stack manually.
Sets the Z axis direction in which the stage will move during acquisition.
 Z-Stack Bottom and Top
Z-Stack Bottom and Top Defines a Z-Stack simply by its top and bottom positions and step. Use the microscope joystick to find the bottom of the inspected cell, click | Requires: Device: Stage Z |
Sets the top Z position.
 Reset
Reset Discards the Top and Bottom position settings.
Sets the bottom Z position.
Selects the Z-Drive device connected to NIS-Elements.
Defines the range of a single step.
Click this button to use the recommended step size.
 Z-Stack Piezo from Bottom
Z-Stack Piezo from Bottom Defines a Z-Stack to be acquired from the bottom position to the top using just the Piezo Z drive. Find the bottom of a cell and capture a Z-Stack with the full range of the Piezo Z drive. See also Z-Stack > | Requires: Device: Stage Z |
Name of the task.
Defines the size of the Z-Stack from the bottom to the top. Check Maximum to use the maximum possible distance.
Defines the range of a single step.
Click this button to use the recommended step size.
Displays information about the number of defined steps.
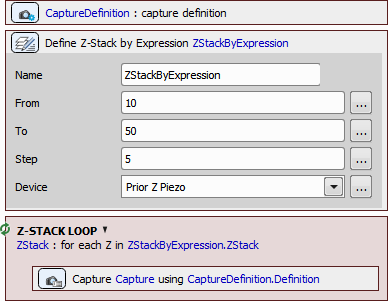
 Z-Stack by Expression
Z-Stack by Expression Defines a Z-Stack using absolute coordinates or variables available in NIS-Elements. Use the button to insert variables into the particular edit box. Use this task when you need to define a Z-Stack with absolute Z positions inserted from variables. | Requires: Device: Stage Z |
Name of the task.
Absolute Z position where the Z-Stack will start.
Absolute Z position where the Z-Stack will end.
Defines the range of a single step.
Selects the preferred Z-Drive device connected to NIS-Elements.
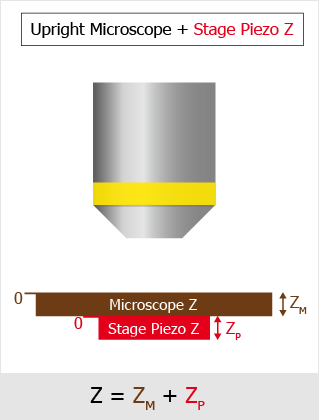
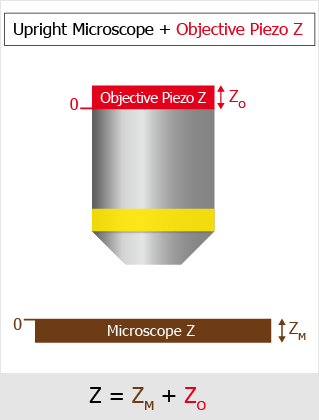
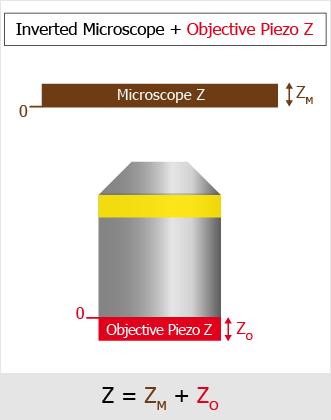
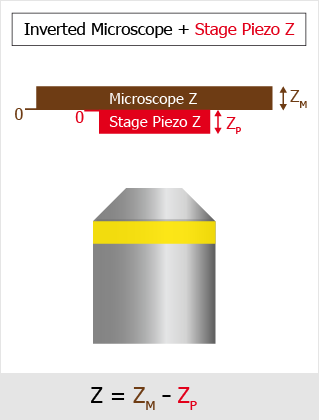
Global Z Coordinates Use Case
In this following example with an inverted microscope, the stage Piezo Z moves against the direction of the microscope Z-drive and the global coordinates are subtracted. To capture a Z stack for global Z coordinates 10 to 50, the microscope Z-Drive goes to 110 and the Stage Piezo Z goes to 100 (global Z coordinate is 110-100 = 10). Then the Stage Piezo Z moves from 100 to 60 so the final global coordinate is 110-60 = 50.
The drawings below show how the global Z value is calculated for different types of Z-devices on different microscopes.
 Z-Stack Loop
Z-Stack Loop Repeats the contained tasks for each Z position of the selected Z Stack. This task can be used inside any other loop (time-lapse, point set) with Acquisition > | Requires: Device: Stage Z |
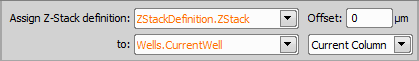
 Assign Z-Stack to Point/Well/ND Acquisition
Assign Z-Stack to Point/Well/ND Acquisition Every XY position (well, row of wells, column of wells) can have unique Z stack parameters after using this task. Scan a wider Z stack over the wells selected by the analysis. | Requires: Task: Z-Stack > Device: Stage Z |
Select your Z-Stack definition for the assignment.
Add an optional Z offset on top of the Z-Stack definition.
Select to which the Z-Stack definition will be assigned. If a second combo box appears (e.g. when using well plates) - specify your selection.
 Move to Z-Stack home
Move to Z-Stack home Moves the Z drive to the home position of the selected Z stack definition. When capturing multi-channel Z-stacks, not all the channels are required to contain the Z dimension. These are usually captured in the home (center) position. | Requires: Device: Stage Z |
Choose your Z-stack definition from your current job.
Moves the Piezo Z device to the position selected in the Position drop-down menu and compensates the second Z-device to stay on the same Z plane as before. Find the bottom of a cell, reset the Piezo Z bottom position and capture a Z-Stack of the cell using the full range of the Piezo Z drive. | Requires: Device: Stage Z |
Name of the task.
Select the position to which the Piezo Z drive moves. The second Z drive compensates for this movement to stay on the same plane. If the Custom option is selected, an exact Z position can be entered into the field. Range displays the possible Z values falling into the current range of the device.


 Capture
Capture
 ND Acquisition
ND Acquisition Loop over Points
Loop over Points Loop over Wells
Loop over Wells