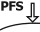
 PFS On and Focus
PFS On and Focus Turns the Perfect Focus System (PFS) on and tries to find the PFS focal plane. Make sure the Z drive focal plane is not too far from the PFS focal plane otherwise the task may fail. Use this task in long-term live-cell experiments (timelapses) to solve the axial focus fluctuations in real time. | Requires: Device: Perfect Focus System |
If you check On fail, do the following, more actions can be done when PFS fails. Auto focusing can be done using a selected Autofocus + Focus Surface >  Autofocus Settings task or Z stage can be moved up/down by a specified value.
Autofocus Settings task or Z stage can be moved up/down by a specified value.
 PFS Off
PFS Off This task switches the PFS Off. Use this task in the job to turn the PFS off whenever it is not needed. | Requires: Device: Perfect Focus System. |
 PFS DM In
PFS DM In Puts the Dichromatic Mirror (DM) in the optical path of the Perfect Focus System (PFS). Use this task for conducting experiments that require the exclusion and then returning the dichromatic mirror back in the optical path of the PFS. | Requires: Device: Perfect Focus System. |
 PFS DM Out
PFS DM Out Puts the Dichromatic Mirror (DM) out of the optical path of the PFS. Use this task for conducting experiments that require the exclusion of the dichromatic mirror. | Requires: Device: Perfect Focus System. |
 PFS Offset from the current z position
PFS Offset from the current z position Finds a PFS offset for the current Z position and sets it as the current offset. Use this task to ensure that exactly the same Z level will be kept when PFS is switched on. | Requires: Device: Perfect Focus System |
 Auto PFS Focus Setup
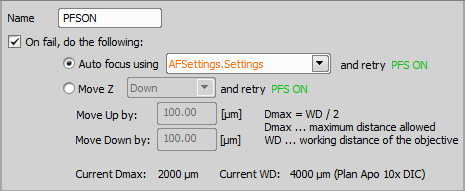
Auto PFS Focus Setup Defines settings to be used by the PFS > Use this task to set up the Auto PFS offset. | Requires: Device: Perfect Focus System Stage Z |
Select the focus criterion based on the nature of your specimen.
 Auto PFS Focus
Auto PFS Focus The PFS system searches for the most in-focus plane and sets the PFS offset accordingly. This task uses settings defined by the PFS > Use this task for creating a PFS surface. | Requires: Device: Perfect Focus System, Stage Z |
See Creating PFS Surface for a sample use case.
 Assign PFS to Point/Well
Assign PFS to Point/Well Uses the current Z position to specify PFS offset for the selected XY position (e.g. a well). Use this task inside a loop over XY points after PFS > | Requires: Device: Perfect Focus System |
Select one of your sample holder positions.
See Creating PFS Surface for a sample use case.
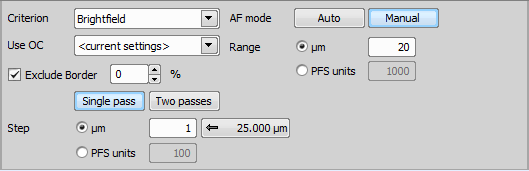
 Create PFS Surface
Create PFS Surface Calculates the global PFS surface from an existing set of PFS positions. To XY positions without the PFS position defined, the PFS position of the closest XY point (which includes PFS position) is copied. Use this task for creating a global PFS surface. | Requires: Device: Perfect Focus System, Motorized Stage |
See Creating PFS Surface for a sample use case.
Any position on the resulting surface is a result of interpolation.
Value of the nearest control point position is taken.
 Move to PFS Surface
Move to PFS Surface Changes the current PFS offset value to match the calculated PFS surface. Use this task in the job whenever it is needed to move to the PFS surface. | Requires: Device: Perfect Focus System, Motorized Stage |
 Offset PFS Surface
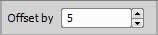
Offset PFS Surface Modifies an existing PFS surface by adding / subtracting an offset distance. Use this task to modify the current PFS surface by a specified value. | Requires: Device: Perfect Focus System, Motorized Stage |
 Detect Well Bottom Material using PFS
Detect Well Bottom Material using PFS This task detects the Z position of the well bottom surfaces and well bottom material (glass/plastic). The detected values are available as task properties. Use this task to detect the well bottom material and the exact well bottom Z position which can then be used by the System > | Requires: Device: Perfect Focus System, Motorized Stage |
 Loop over Wells
Loop over Wells Loop over Points
Loop over Points
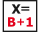 Expression
Expression