Tabs for switching between the layouts.
Opened images displayed as tabs. Each image has its own tool bar. See Image Window.
The
 Acquisition
Acquisition  panel.
panel.The panel for switching of hardware settings, also called lightpaths. Control panels of devices active in the selected lightpath are displayed below. See
 Acquisition
Acquisition  Panel.
Panel.LUTs control panel (
 LUTs).
LUTs).Sample navigation panel (Sample navigation).
ROI Statistics, Intensity Profile and Measurements analysis panels (Analysis Panels).
Customizable shortcuts to advanced functions.
Camera and Illumination control panel.
Microscope control pad (Microscopes).
The  Menu button in the top tool bar displays or hides the main menu.
Menu button in the top tool bar displays or hides the main menu.
Click  RMB on the Compact tab to display a menu with the following options:
RMB on the Compact tab to display a menu with the following options:
Default mode
Adds an additional column with the Device Control panel.
Selects between the previous two modes automatically based on the monitor width.
Select which layout to open after the software starts.
See Modifying Layouts.
This panel is used to quickly modify color and brightness of the image using Look-Up Tables (LUTs). Simply drag the left or the right triangle to adjust the input intensity range. Lift or drop the yellow point to adjust the Gamma parameter. Double-click into the graph area to zoom the histogram so that the “high” and “low” limits are distinguishable. For more details about LUTs, please see LUTs - Non-destructive Image Enhancement.
If turned on, LUTs are applied to the current image.
 Keep Auto LUTs
Keep Auto LUTs Click this button to run the Auto LUTs permanently on the live image (see below).
 Auto LUTs
Auto LUTs This button adjusts the white slider position of all channels automatically with the purpose to enhance the image reasonably.
 Reset LUTs
Reset LUTs Discards all LUTs settings and turns LUTs OFF.
 Settings
Settings Opens the Auto Scale Settings where the Low and High fields determine how many of all pixels of the picture are left outside the sliders when Auto LUTs are applied (0-10%). Check Use Black Level to ensure that the black slider is influenced by the auto scale functions.
 Pixel saturation indication
Pixel saturation indication If turned on, all pixels in the image with values reaching maximal values are highlighted red.
 In Color / Mono
In Color / Mono Switches the single channel image between the color and monochrome view mode.
 Zoom
Zoom Use mouse wheel to zoom the graph. This button jumps to the last zoomed position.
Tip
Double-click in the graph to zoom the input intensity range.
This panel shows statistics - Mean (Min, Max) - for the drawn ROI.
 Draw Rectangle
Draw Rectangle Click and drag in the image to draw a rectangular ROI. To move the ROI, click on its center and move it around. Drag its edge to resize it.
 Draw Circle
Draw Circle Click and drag in the image to draw a circular ROI. To move the ROI, click on its center and move it around. Drag its edge to resize it.
 Draw Polygon
Draw Polygon Click points in the image to define the polygonal ROI. Use the secondary mouse button or a double-click to place the last node of the polygon and close the object. To draw a free-hand shape, hold down the primary mouse button. To move the ROI, click on its center and move it around.
 Reset
Reset Clears all ROIs in the image.
 Measure
Measure Measures the intensity of the whole image or inside the drawn ROI(s) on the selected channel and shows the measured data in the table above. The intensity measurement against the image dimension (Z-Stack, Timelapse) is displayed in the graph below. Select the measured channel from the drop-down menu on the left.
If checked, this function automatically measures intensities right after ROI changes are made.
This panel is used for interactive intensity measurements. An arrow is shown in the image indicating the profile cross section. This cross section intensity is shown in the graph. The profile line can be resized by dragging its ends by mouse arbitrarily. It is always a straight line. Context menu over the arrow allows you to Reverse Direction of the arrow, edit Line Properties (color, width and style), change the Intensity Profile Properties (described below) and to choose which channel is used for the measurement.
Click into the graph to define the maximum.
Click again into the graph to define the minimum.
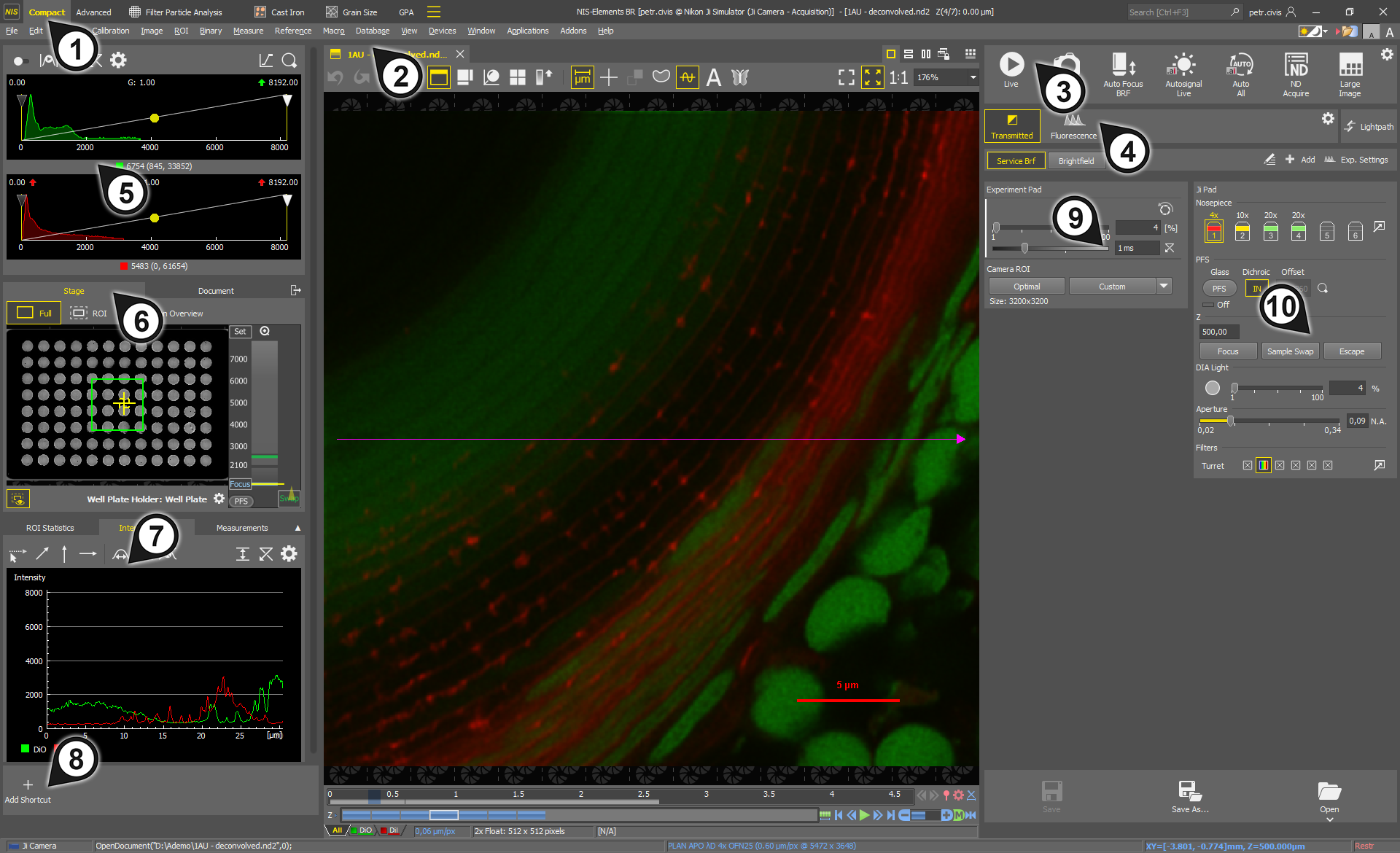
Half of this interval defines the value in which the graph width will be measured.
 Draw Free Line
Draw Free Line Click and drag directly in the image to draw a profile line.
 Free Line
Free Line Insert a profile line which can be freely positioned.
 Vertical Line
Vertical Line Inserts a vertically fixed profile line.
 Horizontal Line
Horizontal Line Inserts a horizontally fixed profile line.
 FWHM
FWHM This tool measures the Full Width at Half Maximum (FWHM) value on the given graph range.
Note
If the minimum is defined in a different part of graph (e.g.: different peak), the width is measured on the peak where the maximum value was defined.
 Auto FWHM
Auto FWHM Measures the FWHM value automatically once this button is clicked.
 Realtime Auto FWHM
Realtime Auto FWHM Measures the FWHM value continually on the live image.
 Vertical Autoscale
Vertical Autoscale Zooms the graph so that both minumum and maximum values are visible.
 Reset
Reset Resets any zoom changes.
 Settings
Settings Opens the Intensity Profile Properties dialog window where you can set the graph interpolation type and the width of the line neighbourhood used for the visualization of the mean/max intensity values.
This panel enables the user to perform simple measurements on the current image.
 Pointing Tool
Pointing Tool Use this tool for selecting measurement objects in the image.
 Simple Line
Simple Line Line length is measured. Click and hold the primary mouse button over the starting position and drag to the ending position and release the button. Confirm the object by the secondary mouse click.
 Polyline
Polyline Polyline length is measured. A polyline consists of several line segments. Use the primary mouse button to draw the line segments. Each mouse-click creates a new node. Complete the total length definition by the clicking the secondary mouse button.
 Polygon
Polygon EqDiameter of a polygon is measured. Draw a polygon by clicking the primary mouse button inside the image. The secondary mouse button or a double-click will place the last node of the polygon and close the object. To draw a free-hand shape, hold down the primary mouse button. Confirm the object by the secondary mouse click.
 Autodetect Polygon
Autodetect Polygon EqDiameter of a detected object is measured. The system automatically detects a homogeneous area around the clicked point.
 Count
Count Click inside the image to insert counted points. A red cross is inserted to the image after each click. Right-click to the image to finish counting.
 Clear Overlay
Clear Overlay Deletes all measurement objects from the image.
 Clear All
Clear All Deletes both the measurement objects and the measurement table.
 Export Data
Export Data Exports the results table into a .csv file.
Shortcuts
Clicking on the button opens a window where you create a shortcut to any function available in the main menu.
Click the button.
Type the name of a menu command into the search field and select one of the search results.
Below, you can change the icon and the tool tip text of the shortcut.
Confirm creation of the shortcut by .
Note
Right-click a created shortcut and select Remove to remove it from the panel.
This panel gathers acquisition and hardware control.
A431
BSC_1
CHOK_1
Cos7
Day1_iPS_neuro
Day4_iPS_neuro
Day7_iPS_neuro
Hela
HepG2
HT29 J774_1
Neuro2a
 Live
Live Displays the live camera image according to the camera settings (the button changes to Freeze when the live image is shown).
The Smart Live function can be enabled in the  Configure... menu. It works only on Fluorescence experiments. It checks the hardware status, including stage movement and changes in the light power. Then it captures all channels if a hardware change affecting all channels has been made beforehand, such as a movement in XY or Z. However, if a change affecting only one channel has been made (e.g., a change in the power of the associated laser line), the other channels remain unchanged. Once the experiment channel(s) are captured, the light is deactivated. This ensures the convenient access to a multichannel live image without causing bleaching to the sample.
Configure... menu. It works only on Fluorescence experiments. It checks the hardware status, including stage movement and changes in the light power. Then it captures all channels if a hardware change affecting all channels has been made beforehand, such as a movement in XY or Z. However, if a change affecting only one channel has been made (e.g., a change in the power of the associated laser line), the other channels remain unchanged. Once the experiment channel(s) are captured, the light is deactivated. This ensures the convenient access to a multichannel live image without causing bleaching to the sample.
 Auto Focus
Auto Focus Performs the fastest possible auto focus. There are two focus ranges available, short and long. By default, the short range is used. Hold the Shift key and click on the  Auto Focus button to use the long range (
Auto Focus button to use the long range ( ).
).
The criterion for focus detection is dynamically changed based on the selected light path (modality).
A criterion suitable for fluorescence samples.
Suitable for brightfield samples. Brightfield auto focus works based on the values set in  Devices > Service Settings
Devices > Service Settings  .
.
Cells.ai Criterion An AI-based algorithm suitable for brightfield cell samples. A specific hardware configuration must be active for this criterion to be available. To switch between the brightfield criterions, use the context menu over the Auto Focus button. The Enable Context Menus option must be selected in the  Configure... menu.
Configure... menu.
The AI neural network has been trained and is intended to be used with the following cell lines:
Note
The Z lens piezo in the system functions with the auto focus only when the register key (HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Laboratory Imaging\Misc\DeviceManagerv2\NosepiecePositionForObjectivePiezo) indicates the nosepiece position where the lens piezo is installed and when it aligns with the current nosepiece position. Please create the registry key “NosepiecePositionForObjectivePiezo” as “DWORD(32bit)”. Set the value in hexadecimal, Position #1 = “0”, Position #2 = “1” ... Position #6 = “5”.
 Autosignal
Autosignal Automatically finds the optimal camera exposure and light power using an AI algorithm. Autosignal.ai has two options for different algorithm strategies:
Tries to be more sensitive to the sample, e.g. by limiting the maximum light power.
Prefers to use more light with short exposures.
To switch between Live Sample and Fixed Sample algorithm, go to the  Configure... menu.
Configure... menu.
 ND Acquire
ND Acquire Opens the standard ND Acquisition window (Combined ND Acquisition).
 Large Image
Large Image Runs the  Addons > Large Images > Scanning Wizard
Addons > Large Images > Scanning Wizard  command used for a step-by-step large image acquisition.
command used for a step-by-step large image acquisition.
 Configure...
Configure... Opens the Acquisition Settings window where settings for the Live, Auto Focus, Autosignal and ND Acquire buttons are adjusted. User can enable or disable context menus and tool tips, and customize which buttons are displayed on the toolbar.
 Save
Save Saves the current image.
 Save As...
Save As... Opens a standard dialog for saving image files.
 Open
Open Displays a standard opening dialog for opening image files.
See Cameras.
See Illumination Devices.
See Other Devices.
Each opened image is shown as a tab. Click on the tab to activate the image or click X to close it.
The navigation tools at the bottom of the image are the same for both layouts and are described here: Control Bar. The top toolbar buttons are described here.
 Undo
Undo Moves one step back through the history of changes.
 Redo
Redo Moves one step forth through the history of changes.
 Auto Calibrate
Auto Calibrate Run the live image and click this button to automatically calibrate your image using the current hardware setup.
 Mouse XY
Mouse XY This feature requires a motorized XY stage. If turned on, the mouse cursor on a live image changes and you can control the XY stage by dragging the live image. Before using this function, it is recommended to perform automatic calibration.
 Split Components
Split Components Turns on a special view, where color channels of the image are displayed separately (tiled). This mode is supported in the modes Main View, Slices View and Volume View.
 Main View
Main View Default viewing mode.
 Show Slices View
Show Slices View This viewing mode displays orthogonal XY, XZ, and YZ projections of the image sequence. It requires a Z or T dimension.
 Volume View
Volume View This view mode creates a 3D model of the acquired object. It requires a Z dimension.
 Show Tiled View
Show Tiled View This view mode displays frames of the selected dimension arranged one next to other. It requires a Z, T or XY dimension. One or two dimensions can be viewed at a time.
 Show Maximum Intensity Projection
Show Maximum Intensity Projection This function analyses all frames of one dimension and picks pixels with the maximum intensity values. These pixels are used in the resulting image. It requires a Z or T dimension.
 Show Scale
Show Scale Displays a line scale which can be moved around the image using the mouse. Context menu over the scale enables the user to Burn Scale into the image permanently, move it to the Default Scale Position, Lock Scale Position or adjust Scale Properties ( View > Layers Properties > Scale Properties).
View > Layers Properties > Scale Properties).
Tip
Use / to show or hide the scale.
 Show Graticule
Show Graticule Displays a graticule layer over the image for quick and approximate measurements. Graticules behave like adjustable floating rulers. User can simply align a graticule with the measured object and read the distance value. Click on the line and drag it to move the graticule. Context menu over the graticule enables the user to move the graticule to the center (Move to Center) and adjust the Graticule Properties.
Tip
Use the * key shortcut to show or hide the graticule layer.
 Show Binary
Show Binary Displays or hides the binary layer in the image.
Tip
Use Ctrl + Up/Down to decrease/increase the binary layer transparency.
 Show ROIs
Show ROIs Displays/hides any ROIs in the image. The ROI Statistics panel is shown below the LUTs control.
 Show Intensity Profile
Show Intensity Profile Displays/hides the intensity profile in the image. The Intensity Profile panel is shown on the left.
 Create EDF Focused Document
Create EDF Focused Document Creates a new simple focused image from an ND file. See Extended Depth of Focus.
 Show EDF Anaglyph
Show EDF Anaglyph Enables/disables the anaglyph 3D view. New options appear in the toolbar - you can define the position of the first frame (Lowest/Highest), Style (the color combination used for anaglyph image), Effect (Descend into the Screen / Rise from the Screen) and Z-zoom (define the percentage).
 Show EDF 3D Surface View
Show EDF 3D Surface View Opens the 3D surface view of the image. See  Applications > EDF > Show Surface View
Applications > EDF > Show Surface View  .
.
 Show EDF Z-Profile
Show EDF Z-Profile Opens the EDF Z-profile panel with the Z-profile graph of the image. See  View > Analysis Controls > EDF Z-Profile
View > Analysis Controls > EDF Z-Profile  .
.
 Show EDF Z-Map
Show EDF Z-Map Creates a new image displaying the EDF Z-map. See  Applications > EDF > Show Z-Map Image.
Applications > EDF > Show Z-Map Image.
 Compare View
Compare View Arranges the two last viewed images next to each other and turns on their dimension and zoom synchronization. The synchronization can be turned off by clicking ![]() Synchronize Views (described below).
Synchronize Views (described below).
 Full Screen
Full Screen Hides all screen elements such as menus, toolbars, etc. and maximizes the image. Only some basic tools for controlling the image stay displayed. Hit Esc to return to the main view.
 Fit to Screen
Fit to Screen Adjusts the zoom factor to view exactly the whole image as big as possible.
 Zoom 1:1
Zoom 1:1 Adjusts the zoom factor so that one pixel of the image matches one pixel of your monitor.
Select a zoom factor from the drop-down menu.
Displays one image at a time.
Arranges all images as tiles ordered to columns.
Arranges all images as tiles ordered to rows.
If turned on, the views of all currently opened images are synchronized (Z position, zoom, etc.). See also Synchronizer.
Opens a panel with all currently opened images shown as thumbnails. Click on an image thumbnail to activate the image.

 Auto All
Auto All