Deconvolution > 3D Deconvolution
Deconvolution > 3D Deconvolution (requires: 3D Deconvolution)
This command setups and runs 3D deconvolution of the current ND image. See 3D Deconvolution .
 Deconvolution > 2D Deconvolution
Deconvolution > 2D Deconvolution (requires: 2D Deconvolution)
This command setups and runs 2D deconvolution of the current image. See 2D Deconvolution.
 Deconvolution > Extract PSF
Deconvolution > Extract PSF (requires: 3D Deconvolution)
Open a sample image containing beads with a known diameter and run the PSF Extractor to generate the point spread function(s) from the image. Save the extracted PSF file and load it using the Import PSF function inside the Deconvolution dialog (see Import PFS... in 3D Deconvolution ). For more information about capturing beads, please see Determining the Point Spread Function (PSF).
Image channel from which the PSF will be extracted.
Physical diameter of the beads used in your sample image.
Number of layers in which the PSF will be detected. The more layers you define the more point spread functions will be extracted and shown in a multi-point image.
Start with the default value. If the result is not satisfying (e.g. when the sample contains a lot of noise particles with a similar size as the beads) try to lower the value.
 Deconvolution > Show Live De-Blur Setup
Deconvolution > Show Live De-Blur Setup (requires: 2D Deconvolution)
This command defines the settings for de-blurring of live image. See Live De-Blur Setup.
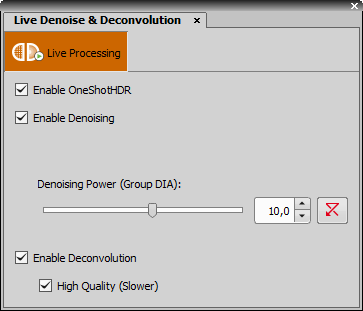
 Deconvolution > Live Denoise & Deconvolution
Deconvolution > Live Denoise & Deconvolution (requires: 2D Deconvolution)
Runs denoising and deconvolution on the live image calculated by GPU (graphics card). The pull-down menu next to the function button shows/hides the Live Denoise & Deconvolution dialog window.
 Live Processing on Primary Camera
Live Processing on Primary Camera State of this button indicates whether the live processing is performed (orange color) or not.
Enhances the dynamic range on the currently captured image.
Check this option to enable image denoising (removing any image noise). Check the channel(s) which should be denoised and set the Denoising Power.
Check this option if you want to run the fastest deconvolution method on the live image.
Decide whether you prefer quality to speed. A simpler and faster algorithm is used if this option is deselected.