Applications > HDR > Capture Reflection Free Image
Applications > HDR > Capture Reflection Free Image (requires: High Dynamic Range)
This command starts the Capture HDR Image function with all settings calculated automatically. The algorithm starts from the current exposure, finds high and low exposure times and the step count. As a result the application creates a standard (not multichannel/multiexposure) image.
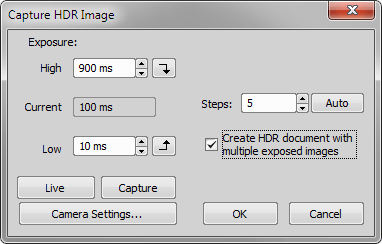
 Applications > HDR > Capture HDR Image
Applications > HDR > Capture HDR Image (requires: High Dynamic Range)
Captures a high dynamic range image. Press to capture the HDR image according to the settings.
Set the highest and the lowest exposure values to be included in the capturing. The buttons next to the edit fields enables you to try the exposure times in live image (the buttons set the defined exposure time as current).
the maximum exposure time
indicates the current exposure time on live
the minimum exposure time
Define the number of steps for HDR capturing - how many frames the HDR image will be calculated from. Use the button to calculate optimal number of the steps for the current exposure range.
Select this option to create a multichannel image. Each channel will be named according to the exposure time used to capture it.
Starts live image.
Performs standard Capture command (not the HDR capture).
Displays the Camera Settings control window.
 Applications > HDR > Create HDR from Current ND
Applications > HDR > Create HDR from Current ND (requires: High Dynamic Range)
This command creates a HDR image from a ND2 file. The new HDR image opens in a separate window.
 Applications > HDR > Create HDR Image from File
Applications > HDR > Create HDR Image from File (requires: High Dynamic Range)
Selects source files for creating an HDR Image. The new HDR image opens in a separate window. If you check the Create Multiexposure Document option, a multichannel image is created.
 Applications > HDR > Apply One-Shot HDR to Current Image
Applications > HDR > Apply One-Shot HDR to Current Image (requires: High Dynamic Range)
Opens the Apply One-Shot HDR dialog window used for enhancing the dynamic range on the currently opened image.
 Applications > Filter Particle Analysis > Start Application
Applications > Filter Particle Analysis > Start Application 
(requires: Filter Particle Analysis)
This command runs the Filters module. See Filter Particle Analysis for detailed description of all features of the module.
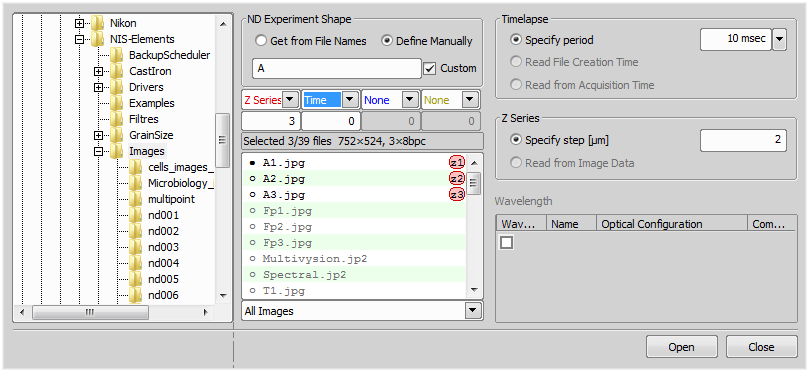
Specify the folder which contains the sequence of images.
Select ND Experiment Shape.
Set the dimensions of ND2 file (Time, Z Series, Wavelength, Multipoint). Specify number of dimension frames in the file sequence in the field below.
Select the file which will represent a first frame in ND2 file by double-clicking its name or click on the point before the file name.
Display the focused image.
Select the Edit Area in Focused Image command.* The cursor changes.
Draw an area inside the focused image which should be affected. Finish drawing by right-click.
Use the mouse wheel or arrow keys to browse Z slices within the area.
Finish the procedure by right-click or Enter.
 Applications > EDF > Create Focused Image
Applications > EDF > Create Focused Image 
(requires: EDF Module)
When the method is selected and the sequence is aligned, the only thing to do is to run the  Applications > EDF > Create Focused Image
Applications > EDF > Create Focused Image  command. The focused image will be created and appended to the ND2 file (when the ND2 file is saved to disk the focused image is included).
command. The focused image will be created and appended to the ND2 file (when the ND2 file is saved to disk the focused image is included).
Z-Map Setting
Sets the method for the Z reconstruction. This reconstruction takes all Z slices and their focused image to create a 3D model of the whole scene called Z-Map. The Balanced method brings more consistent results with less noise and artifacts when compared to the former faster method (Original). If the Z-map calculation is not necessary for your task, select None to speed up the EDF image acquisition.
Places the lowest Z slice in the zero level, e.g. for better interpretation.
The original absolute Z coordinates remain intact.
Check this option if you do not want to see this dialog in the current session again.
 Applications > EDF > Create Focused Document
Applications > EDF > Create Focused Document 
(requires: EDF Module)
Creates a new document containing one EDF focused image (Z-stack from the source image is merged into a single frame).
 Applications > EDF > EDF Z-Profile
Applications > EDF > EDF Z-Profile 
(requires: EDF Module)
Measures within the Z-profile graph. Please see the description of the  View > Analysis Controls > EDF Z-Profile
View > Analysis Controls > EDF Z-Profile  .
.
 Applications > EDF > Show Anaglyph
Applications > EDF > Show Anaglyph 
(requires: EDF Module)
This command displays the anaglyph view of the current data-set. The focused image must have been created before. See Extended Depth of Focus.
 Applications > EDF > Show Surface View
Applications > EDF > Show Surface View 
(requires: EDF Module)
This command displays the surface view of the current data-set. The focused image must have been created before. See Extended Depth of Focus.
 Applications > EDF > Open File Sequence
Applications > EDF > Open File Sequence (requires: EDF Module)
This command opens a sequence of images and creates an ND2 file out of it.
Dialog options
Mark this button to define ND2 file from file names.
Mark this button if you want to define the files manually.
If you want to edit the name pattern manually, check this item and the text field on the left side of this option becomes editable. Edit the text or enter a new name pattern.
Set Timelapse period value. Specify the exact value from the pull down menu or select to use File Creation Time or Acquisition Time.
Set Z Series step as value (µm) or select to use the Z Series step from Image Data.
Define name of the channel. Define name of the existing optical configuration or start defining a new one. Choose one of the seven predefined colors or brightfield option as a color of the channel. You can also select the More option to define a custom channel color.
Opens the selected sequence of image as a ND2 file according to the given properties.
 Applications > EDF > Align Sequence
Applications > EDF > Align Sequence (requires: EDF Module)
This command aligns the current Z series in order for the EDF to work properly.
 Applications > EDF > Edit Area in Focused Image
Applications > EDF > Edit Area in Focused Image (requires: EDF Module)
This advanced option enables you to draw an area inside the image and select the Z slice to be used in the resulting focused image.
* - when you have the area defined, the selection can be inverted by pressing G.
 Applications > EDF > Edit Background
Applications > EDF > Edit Background (requires: EDF Module)
This function enables the user to handle the background of a Z-series surface image viewed in the Show EDF 3D Surface View ( Applications > EDF > Show Surface View
Applications > EDF > Show Surface View  ). After the focused image is created, you can invoke this command. The following dialog appears:
). After the focused image is created, you can invoke this command. The following dialog appears:
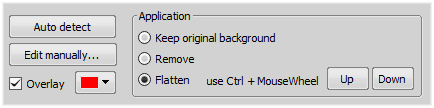
First, you have to detect the background. Click to perform the auto detection. If the results are not fully satisfying, or in any other case, choose to open the ROI editor. Detect the background using the tools available and then press the Tab key or click to close the editor.
See Binary Editor.
Check Overlay and set the color of the overlay for better visualization of the edited layer.
Finally choose how to process the background in the Application section. Remove option deletes the detected background area. Flatten will set all the background Z-coordinates to zero so that the background will form the zero level which can be moved in the Z dimension or . If you do not want any of the mentioned options, select Keep original background.
 Applications > EDF > Show Z-Map Image
Applications > EDF > Show Z-Map Image (requires: EDF Module)
This command displays the Z map of an ND document which contains the Z dimension.
 Applications > EDF > Real Time EDF
Applications > EDF > Real Time EDF 
(requires: EDF Module)
The Real Time EDF command is integrating the whole functionality of EDF. It captures a Z-sequence, aligns the images (optionally), and creates the focused image. When the command is invoked, the Real Time EDF dialog appears. Check, whether to align the images or not. See also Real Time EDF.
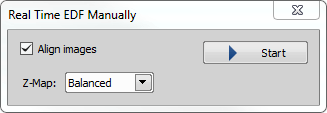
 Applications > EDF > Real Time EDF Manually
Applications > EDF > Real Time EDF Manually (requires: EDF Module)
The Real Time EDF Manually command is integrating the whole functionality of EDF. It makes the focused image from a Z-sequence captured from the Live stream during manual Z movement. When the command is invoked, the following dialog appears. Check, whether to align the images or create a Z-Map and click .
 Applications > Layer Thickness Measurement > Measure Layers
Applications > Layer Thickness Measurement > Measure Layers (requires: Layer Thickness)(requires: Local Option)
Opens the Layer Thickness Measurement dialog window.
 Applications > Metallography > Cast Iron
Applications > Metallography > Cast Iron (requires: Metalo - Cast Iron Analysis)
This command starts the Metallography - Cast Iron application layout. Please see Metalo - Cast Iron Analysis for further details.
 Applications > Metallography > Grain Size
Applications > Metallography > Grain Size (requires: Metalo - Grain Size Analysis)
This command starts the Metallography - Grain Size application layout. Please see Metalo - Grain Size Analysis for further details.
 Applications > Weld Measurement > Measurement Explorer
Applications > Weld Measurement > Measurement Explorer 
(requires: Local Option)
Opens the Measurement Explorer panel.
See also Measurement Explorer.
 Applications > Weld Measurement > Measurement Sequencer - Definition
Applications > Weld Measurement > Measurement Sequencer - Definition 
(requires: Local Option)
Opens the Measurement Sequencer - Definition panel used for the preparation of advanced sequential measurement definitions.
 Applications > Weld Measurement > Measurement Sequencer - Run
Applications > Weld Measurement > Measurement Sequencer - Run 
(requires: Local Option)
Opens the Measurement Sequencer - Run panel used for executing the measurement definitions previously defined in the Measurement Sequencer - Run window.
 Applications > Concrete > Start Concrete
Applications > Concrete > Start Concrete 
(requires: Local Option)(requires: Concrete)
Opens the Concrete application (Concrete).



 Exit Editor
Exit Editor